 Sewage contains a myriad of potentially life threatening chemical and biological matter. This paper shows studying sewage is crucial to understanding its threat, but it can also unlock potential epidemiological information.
Sewage contains a myriad of potentially life threatening chemical and biological matter. This paper shows studying sewage is crucial to understanding its threat, but it can also unlock potential epidemiological information.
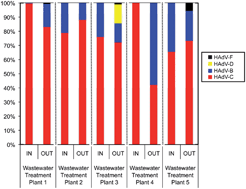
Disposing of sewage appropriately is one of the most important life-saving technologies that exist, however processing such waste poses health risks. Some of the hazards associated with sewage are from adenoviruses, which can be infectious through direct contact, ingestion and aerosol exposure; a particular concern as solid material from sewage plants is often disposed of as agricultural fertiliser. Previous studies have focussed on single adenovirus species or grouped them together; however the seven main species all possess unique symptoms when contracted. Bibby and Peccia have therefore used PCR and primers able to distinguish between the species to amplify DNA from samples of sewage influent and effluent.
The results revealed that the adenovirus-C was most abundant, responsible for respiratory symptoms, followed by adenovirus-B, also associated with respiratory illnesses as well as urinary infections. It should be noted though that increased virus abundance does not necessarily correlate with increased infectious risk. Interestingly, wastewater treatment had no impact on the virus numbers, showing treated solid waste, spread on agricultural land, poses an equal risk as raw influent from adenoviruses.
Whilst providing information for risk assessments this data also lends support to the notion that sewage contains a great amount of information regarding its source population, negating the need for, and potential flaws in, medical data. In this case, adenovirus C and B, the most abundant in the sewage, are also the most abundantly reported infections within the population.
This work is of interest to a variety of people including those involved in human health risk assessments, gene amplification, sewage treatment and disposal and sewage epidemiology it’s free to access* on our site for the next four weeks, so why not download the paper here:
Prevalence of respiratory adenovirus species B and C in sewage sludge
Kyle Bibby and Jordan Peccia
DOI: 10.1039/c2em30831b
*Free access to individuals is provided through an RSC Publishing personal account. Registration is quick, free and simple
Published on behalf of Sian Evans, Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts web science writer. Sian is a PhD student based in Bath, United Kingdom