When investigating dyes, we almost always address the molecular system experimentally in a solution, and theoretically in the gas phase. Greisch and co-workers circumvent this problem by doing both in condensed phases as well as the gas phase. To me, it explained a phenomenon that I have come across several times: the >1800 cm-1 shift between ab initio calculated transition energies and the observed spectra. A difference e.g. ZINDO methods is compensated for, and why these are the tinctorial chemist’s choice when predicting spectra from molecular structures. With this paper it is demonstrated that if you want to design gas phase dyes, DFT calculations can be used.
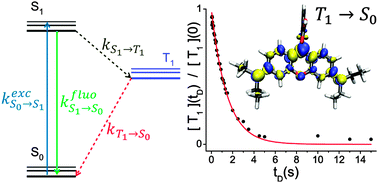
The focus of the paper is the triplet energy, triplet lifetime and triplet deactivation of rhodamine dyes, addressing their use in STED super-resolution microscopy and the triplet state mediated photodegradation. While that motivation is good, I am too excited about the gas phase fluorescence spectra and their use in benchmarking computational approaches. Emission spectra of isolated ionic dyes, can also answer some of the questions regarding counter ion effects, symmetry and solvation that has been around for half a century. I am eagerly awaiting the next installment promised at the end of this paper.
By Dr Thomas Just Sørensen
Read the full details of this PCCP paper today:
Intrinsic fluorescence properties of rhodamine cations in gas-phase: triplet lifetimes and dispersed fluorescence spectra
Jean-François Greisch, Michael E. Harding, Mattias Kordel, Wim Klopper, Manfred M. Kappes and Detlef Schooss
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15, 8162-8170
DOI: 10.1039/C3CP44362K
This article is part of a collection to coincide with the theme of Bunsentagung 2013: ‘Theory meets Spectroscopy’. You may be interested in the other articles in this collection too.










![Remarks on time-dependent [current]-density functional theory for open quantum systems Remarks on time-dependent [current]-density functional theory for open quantum systems](http://pubs.rsc.org/services/images/RSCpubs.ePlatform.Service.FreeContent.ImageService.svc/ImageService/image/GA?id=C3CP51127H)
 The “New Frontiers of Hydrocarbons” award in the Downstream category has been assigned to
The “New Frontiers of Hydrocarbons” award in the Downstream category has been assigned to