Cancer therapeutics is a burgeoning field of research, particularly because chemotherapy has serious side effects that include the devastation of healthy tissue and the possibility that some cancerous tissue survives the radiation. Research is therefore underway to specifically target cancerous tissue by using targeted drug delivery systems. We know that nanoparticles can accumulate in cancer tissue, and Wei Wang’s group takes advantage of this fact to create a cancer-specific nanoparticle-based drug delivery system.
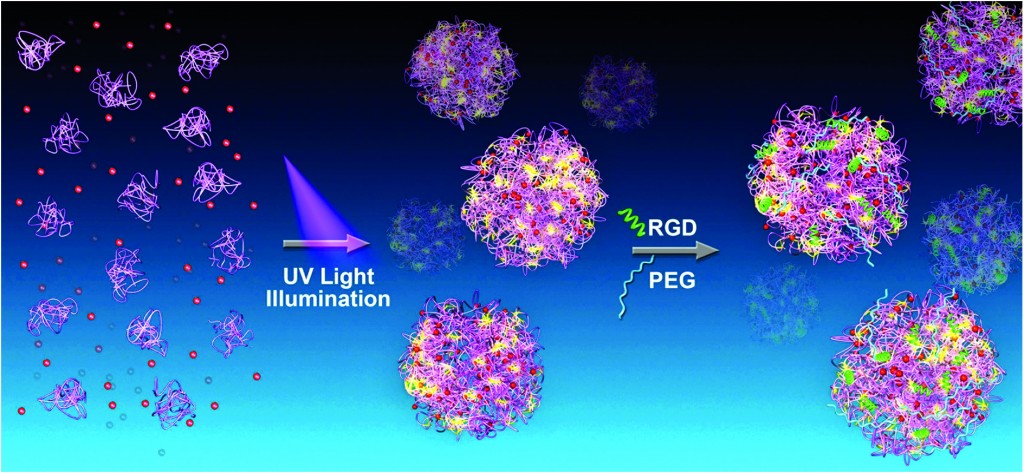
The researchers produce nanoparticles that contain UV-sensitive proteins. When exposed to UV light, the nanoparticle proteins assemble with a cancer drug and a cancer cell-targeting protein fragment. The researchers aim to create a nanoparticle-drug complex that specifically attaches to cancerous cells. When fluorescent nanoparticles were injected into cancerous mice, the researchers found that the particles specifically accumulated in the cancerous tissue. Further, these nanoparticles were able to effectively kill cancer cells in a dish. Finally, the researchers showed that these nanoparticles could decrease the size of a tumor in cancerous mice. This research demonstrates an important breakthrough in cancer treatment.
Photo synthesis of protein-based drug-delivery nanoparticles for active tumor targeting
Jinbing Xie, Ying Li, Yi Cao, Chun Xu, Mao Xia, Meng Qin, Jiwu Wei and Wei Wang
Biomater. Sci., 2013, Advance Article DOI: 10.1039/C3BM60174A
Debanti Sengupta recently completed her PhD in Chemistry from Stanford University. She is currently a Siebel postdoctoral scholar at the University of California, Berkeley.
Follow the latest journal news on Twitter @BioMaterSci or go to our Facebook page.
To keep up-to-date with all the latest research, sign-up to our RSS feed or Table of contents alert.