The rationale for combination therapy is to employ various therapeutic methods which work using different mechanisms, thereby decreasing the chance of developing resistant cancer cells. Photothermal therapy (PTT) is the use of electromagnetic radiation to eradicate cancer cells which can also be utilized to increase the effectiveness of chemotherapy or radiation therapy. The application of targeted and functional nanoparticles can be used to overcome the existing limitations of nonspecific toxicity which is associated with PTT. Therefore, functional nanomaterials with near-infrared (NIR) PTT, high biocompatibility and excellent photothermal conversion efficiency can be dynamic tools for cancer ablation without affecting normal healthy tissue.
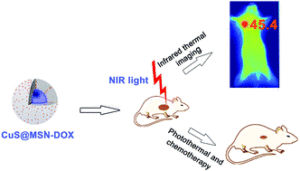
The Chen group used core-shell water-soluble copper sulphide nanoparticles (CuSNPs) coated with mesoporous silica nanoshells (MSNs) for effective delivery of anti-cancer drug doxorubicin (DOX) towards H22 liver cancer. Cleverly, the hollow cavity of MSN was utilized for the loading of anti-cancer drug DOX. CuS@MSN-DOX demonstrated good water dispersibility, high stability, excellent biocompatibility and strong NIR absorption. Its excellent photothermal and NIR thermal imaging properties are due its strong NIR photothermal conversion efficiency. The anti-tumor activity of CuS@MSN-DOX was extensively studied in both in vitro and in vivo therapeutic models which supports excellent chemotherapeutic activity. Complete eradication of the liver tumor was observed by combination therapy of PTT and chemotherapy using CuS@MSN-DOX. Infrared thermal imaging was used to monitor the photothermal treatment. These results clinically validate the multifunctional cancer theranostics property of CuS@MSN-DOX that has enormous potential for clinically translatable thermochemotherapy and enhanced drug delivery in the future.
Biocompatible CuS-based nanoplatforms for efficient photothermal therapy and chemotherapy in vivo Biomater. Sci., 2017, 5, 475 – 484
Dr. Sudip Mukherjee is a Web Writer for Biomaterials Science. He is currently a Postdoctoral Research Associate working alongside Dr. Omid Veiseh at the Department of Bioengineering at the Rice University. His research is involved in the development of advanced nanomaterials for drug/gene delivery in cancer theranostics, immunomodulatory applications & angiogenesis. He published a total of ~30 research articles/patents. He serves as International Advisory Board Member for‘Materials Research Express‘, IOP Sciences. He is an associate member (AMRSC) of RSC, UK. He serves as reviewer for several international journals like Chem Comm, J Mater Chem A, J Mater Chem B, Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, RSC Advances, IOP Nanotechnology etc.
Contact Email: sudip.mukherjee@rice.edu