Test for methylarginines in newborn infants
Developing an analytical technique for use in the field of neo-natal intensive care presents a significant challenge to researchers. Newborn infants who are very premature and unwell can’t safely provide large blood samples for analysis, and a fast turn-around of lab results is crucial for a life-saving diagnosis.
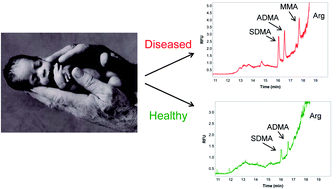
Methylarginines (MAs) are nitric oxide synthase inhibitors which have been linked to respiratory problems in newborns. Researchers led by Susan Lunte at the University of Kansas, USA, report the use of capillary electrophoresis (CE) to measure and track methylarginine concentrations in infant blood plasma for the first time. Their newly developed sample preparation and separation methods are specifically designed to cope with low volume plasma samples, and the results confirm that infants in neo-natal intensive care units (NICUs) have extremely high MA levels.
Click the link below to read more… This article will be free to access until June 7th.
Determination of methylarginines in infant plasma by CE-LIF
Thomas H. Linz and Susan M. Lunte
Anal. Methods, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4AY00340C