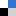
Olive oil/nanoparticle degradation by lipase activity
Researchers in Mexico present a new rapid and cost effective spectrophotometric method to determine lipase activity in olive oil.
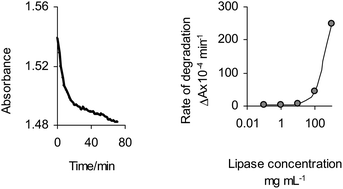
Lipases are a group of enzymes which catalyse reaction of hydrolysis of triacylglycerols to give free fatty acids, monoacylglycerol and glycerol. Measuring their activity is important in medicine and diagnostics as well as in pharmaceutical, cosmetic and paper industry. Unfortunately, the conventional assays currently available still rely on time-consuming procedures and employ radioactive materials and expensive reagents. In this work, the researchers used a layer of triglyceride coated with Fe2O3 nanoparticles which are released when the substrate is degraded. A consequent change in light absorbance is observed following substrate degradation.
The new spectrophotometric method introduced by Margarita Stoytcheva and her group represents a promising analytical approach to reduce cost and increase effciency.
To read the full article, please access the link below. The paper will be free to read until March 18th.
A spectrophotometric lipase assay based on substrate–nanoparticle assembly degradation
Margarita Stoytcheva , Roumen Zlatev , Samuel Behar and Jean-Jacques Bois
Anal. Methods, 2013, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C3AY00044C