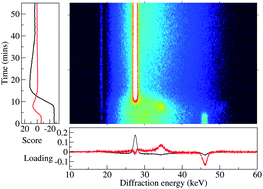
 Jonathan C. Burley and co-workers from the UK demonstrate, for the first time, the application of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to the analysis of time-resolved energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction data. Such a new strategy for the analysis of large sets of diffraction data is needed with the increasing use of in situ diffraction for following a variety of chemical processes. PCA is shown to offer significant advantages over traditional curve-fitting methods in terms of speed and lack of potential user bias.
Jonathan C. Burley and co-workers from the UK demonstrate, for the first time, the application of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to the analysis of time-resolved energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction data. Such a new strategy for the analysis of large sets of diffraction data is needed with the increasing use of in situ diffraction for following a variety of chemical processes. PCA is shown to offer significant advantages over traditional curve-fitting methods in terms of speed and lack of potential user bias.
Interested in knowing more? Read for free until April 4th.
The application of statistical methodology to the analysis of time-resolved X-ray diffraction data
Jonathan C. Burley, Dermot O’Hare and Gareth R. Williams
Anal. Methods, 2011, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C0AY00772B