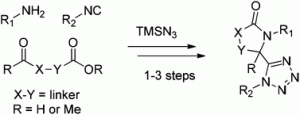
The classical Ugi multi-component reaction can be used to generate a peptidic-like molecule, with 4 points of diversification, from an aldehyde, an amine, an isocyanide and a carboxylic acid. In the Ugi-azide reaction, the carboxylic acid is replaced with trimethylsilyl azide, providing a convenient route to 1,5-disubstituted tetrazoles. This scaffold is a bioisostere for the cis-amide bond.
In the HOT article, Gunawan and Hulme report the use of Ugi-azide reactions to generate a series of different bis-hetrocyclic tetrazolo scaffolds, facilitated by variation of the linker group in the aldo/keto-acids/esters. These scaffolds may aid the development of new molecular probes for the investigation of peptidergic biological systems.
Bifunctional building blocks in the Ugi-azide condensation reaction: a general strategy toward exploration of new molecular diversity
Steven Gunawan and Christopher Hulme
DOI: 10.1039/C3OB40900G
Free to access for 4 weeks