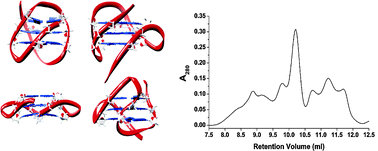
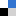 This hot article from John O. Trent et al. at the University of Louisville describes a method for using size exclusion chromatography (SEC) to determine polymorphism in G-quadruplexes. Current methods for investigating polymorphism rely on modification at either the 3′ or 5′ ends of the sequence, shortening or lengthening putative loop regions to try to produce an enriched configuration to study. But this manipulation of the equilibrium may result in the creation of unnatural species that are not present in vivo.
This hot article from John O. Trent et al. at the University of Louisville describes a method for using size exclusion chromatography (SEC) to determine polymorphism in G-quadruplexes. Current methods for investigating polymorphism rely on modification at either the 3′ or 5′ ends of the sequence, shortening or lengthening putative loop regions to try to produce an enriched configuration to study. But this manipulation of the equilibrium may result in the creation of unnatural species that are not present in vivo.
Trent’s method allows the separation and analysis of quadruplex species without any of the above modifications and has been demonstrated successfully in ten promoter sequences:
Polymorphism and resolution of oncogene promoter quadruplex-forming sequences
M. Clarke Miller, Huy T. Le, William L. Dean, Patrick A. Holt, Jonathan B. Chaires and John O. Trent
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2011, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C1OB05891F