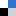This month, our outside cover illustrates an article written by Dr Zdeněk Sofer (Institute of Chemical Technology, Czech Republic) and his colleagues, focusing on graphite oxides.
This month, our outside cover illustrates an article written by Dr Zdeněk Sofer (Institute of Chemical Technology, Czech Republic) and his colleagues, focusing on graphite oxides.
In their paper, the authors show that more complex products (large amounts of complex ions) than water vapor and carbon mono- and dioxide are produced during the exfoliation process. The team came to the conclusion that the full understanding of the exfoliation mechanism and products is crucial for reproducible scalable synthesis of reduced graphenes on a large scale.
Carbon fragments are ripped off from graphite oxide sheets during their thermal reduction
Ondřej Jankovský, Štěpánka Hrdličková Kučková, Martin Pumera, Petr Šimek, David Sedmidubský and Zdeněk Sofer
New J. Chem., 2014, 38, 5700-5705. DOI: 10.1039/C4NJ00871E
Prof. Kingo Uchida (Ryukoku University, Japan) and his co-workers have designed the inside cover. They focused their research on the development of molecular switches, in particular photoactive systems that are a major challenge in the context of molecular devices and light-responsive systems.
In their paper, they present the synthesis of a diarylethene with an attached malachite green moiety and study the photochromism and halochromism of six states (neutral, mono- and dicationic states under both open- and closed-ring isomeric states) to clarify the effect of combining two dyes. The data obtained will contribute to the design of pH sensitive photoswitches, especially for biological applications and their successful incorporation in various applications and in switchable molecular-based devices.
A photo- and halochromic multicolor switching system consisting of diarylethene and malachite green moieties
Yuto Tatsumi, Noriko Fujinaga, Megumi Kasuno, Masakazu Morimoto, Satoshi Yokojima, Shinichiro Nakamura and Kingo Uchida
New J. Chem., 2014, 38, 5706-5714. DOI: 10.1039/C4NJ00434E
_____________________________________
Also discover a Focus, written by Dr Borkovec (University of Geneva, Switzerland) and his colleagues, dedicated to the intrinsic approach describing microscopic ionization equilibria. The authors present an intrinsic description with examples of increasing complexity, thereby highlighting various strategies to extract the relevant parameters. They also address the notion of group transferability, then the central idea of cluster expansion of the free energy, and finally molecular symmetries and homologous series.
Explore the table of contents of this issue here