
RSC Mechanochemistry has published its first articles. To celebrate this, we asked the authors to discuss their work in some more detail.
In this edition, we hear from Hanusa about their study titled Grinding and the anisotropic environment: influences on the diastereoselective formation of Group 15 allyl complexes.
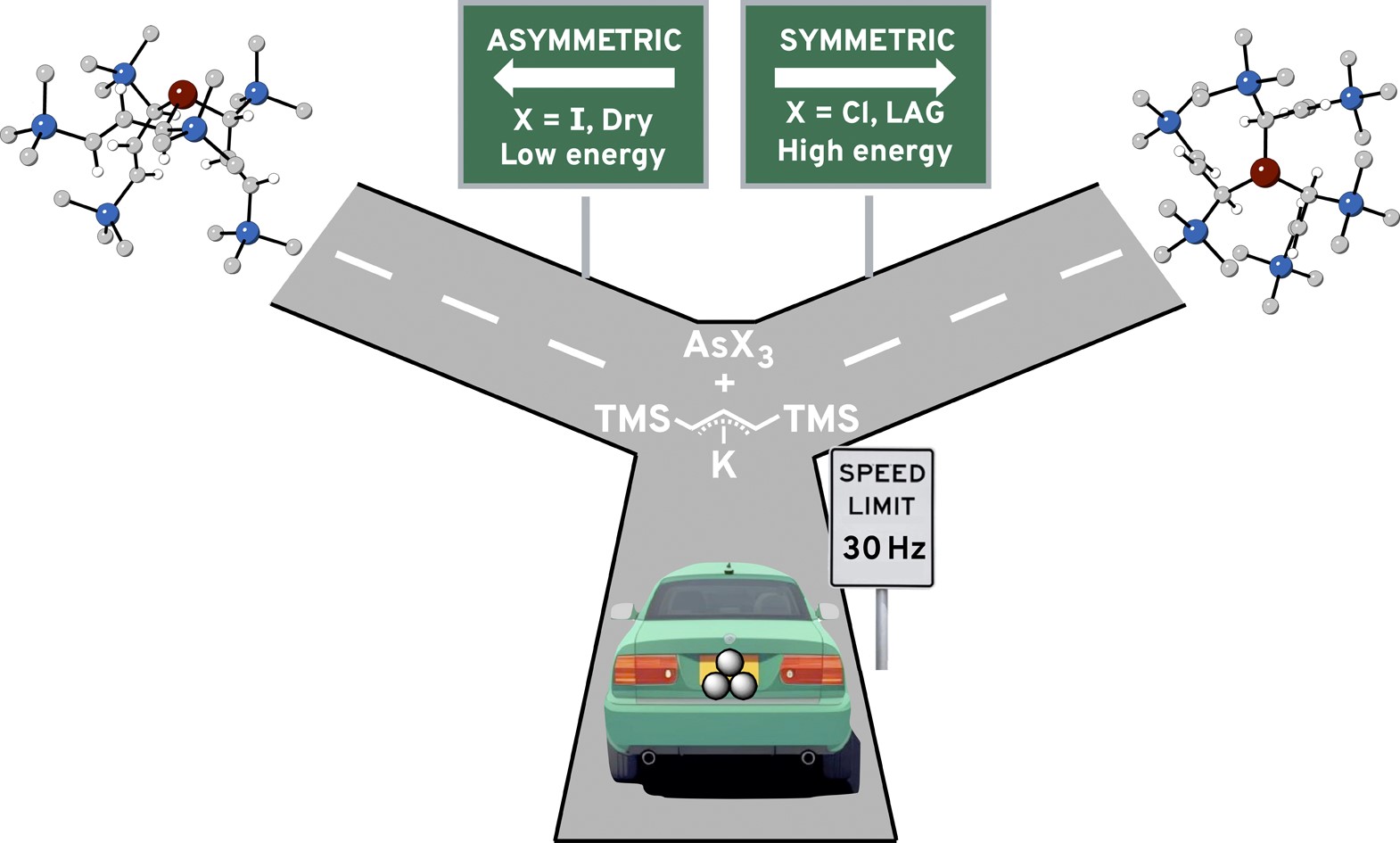
“The environment in a mechanochemically driven reaction is often considered chaotic and random, whether it’s from the pelting of stainless-steel balls or the effect of collisions in resonant acoustic mixing (RAM). So, the possibility of studying a mechanochemical environment that is less than homogenous—that has anisotropic features—is particularly attractive.”
“In this research, we revisited a system we had studied a few years ago, which involved organometallic diastereomers formed either in solution or mechanochemically. In the case of arsenic and antimony complexes with bulky allyl ligands, a greater percentage of the asymmetric form was generated during mechanochemical synthesis. The difference was traced to the use of layered starting reagents, specifically AsI₃ and SbCl₃, and their directing effect on compound formation. In solution, the anisotropic environment is lost, and a larger amount of the more symmetric diastereomer is formed, owing to the quasi-spherical environments around the As³⁺ and Sb³⁺ ions.”
“The current study expanded the range of reagents and mechanochemical variables used to synthesize the diastereomers. The aim was to determine their effect on the diastereomer ratios, yields, and formation of decomposition products. When liquid AsCl₃ was used in place of the layered, solid AsI₃, the diastereomer ratio of the arsenic complex not surprisingly veered toward solution values. However, the strong effect of liquid-assisted grinding (LAG) was unexpected. LAG altered the diastereomer ratio toward solution values, even when minimal amounts of solvents were added, and the reagents had negligible solubility in the added solvent.”
“These results indicate that the anisotropic environment can be meaningfully manipulated in the solid state. Since it is a variable with no direct solution counterpart, such as the time or temperature of the reaction, its expanded use holds promise for new outcomes from mechanochemically initiated synthesis.”
Want to know more about their work? Read the full paper here!
Lauren E. Wenger and Timothy P. Hanusa
RSC Mechanochem. 2024, Advance Article, DOI: 10.1039/D4MR00001C
 |
RSC Mechanochemistry offers you an inclusive and dedicated home for the ideas, scientific language and approaches that cut across the many disciplines mechanochemistry touches. Here we are seeking to build knowledge, as well as foster innovation and discovery at this forefront of chemistry. Whether you are seeking to understand the fundamentals of mechanochemistry, or you are excited by its applications and potential, this journal is for you.
|

