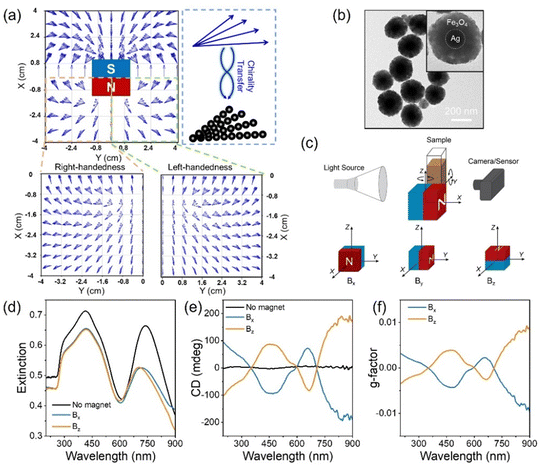
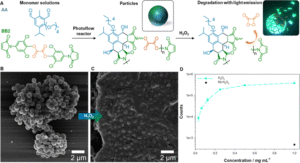
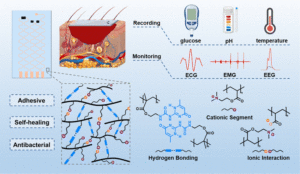
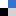Soft wearable sensors
Open call for papers
We are pleased to announce an open call for papers to a themed collection across Nanoscale Horizons and Materials Horizons, published by the Royal Society of Chemistry.

This collection is being guest edited by Professors John Rogers (Northwestern University, USA), Wenlong Cheng (University of Sydney, Australia), Alina Rwei (TU Delft, Netherlands), Dae-Hyeong Kim (Seoul National University, South Korea) and Nanshu Lu (University of Texas at Austin, USA).
Next-generation soft wearable sensors hold significant promise for revolutionizing healthcare and human-computer interaction by providing seamless integration between the human body and electronic devices. These advanced systems, characterized by their flexibility, stretchability, and biocompatibility, enable continuous monitoring of physical parameters such as body motion, physiological parameters like heart rate, and biochemical markers like electrolytes and cortisol levels in sweat in real-time. This real-time data collection can lead to more personalized and timely medical interventions, enabling a shift from hospital-centred healthcare to patient-centred healthcare.
Beyond healthcare, next-generation soft wearable sensors have applications in fitness, sports, and augmented reality (AR)/virtual reality (VR), paving the way for innovative approaches to human performance enhancement and interactive technologies. They offer significant advancements in human-machine interaction, enhancing experiences in the metaverse and beyond. This special issue aims to highlight the latest research, developments, and innovative applications in soft wearable sensors from a materials and nanotechnology perspective, and we believe your work would make a valuable contribution to this discussion.
This special-themed collection aims to provide a platform to showcase the recent progress and challenges in the field of soft wearable sensors addressing the exciting current challenges in biosensors, bioelectronics, medicine, healthcare, AR/VR and soft robotics. The scope of the collection is broad, including but are not limited to:
- Soft wearable materials and design
- Innovative fabrication methods of soft wearable sensors
- Materials and technologies for enhanced sensor performance
- Integration of sensors with wearable systems
- Significance of machine learning and artificial intelligence for remote diagnostics and automatic decision making
- Applications in health monitoring, rehabilitation, AR/VR and sports
- Challenges and future directions in the development of soft wearable sensors
Open for submissions until 14 March 2025
How to submit
Submissions should fit within the scope of either Nanoscale Horizons or Materials Horizons. Please visit the journal webpages for more information on their scope, standards, article types and author guidelines. We invite authors to select the journal that best suits their submission. Please note that primary research is accepted in the form of Communications for both journals and require a ‘New Concepts statement’ to help ascertain the significance of the research. General guidance and examples can be found here.
For Nanoscale Horizons, we welcome exceptionally high-quality studies across all fields of nanoscience and nanotechnology in the form of Communications and Review-type articles (Reviews and Focus articles).
For Materials Horizons, we welcome exceptionally high-quality materials science in the form of Communications and Review-type articles (Reviews, Opinions and Focus articles).
We strongly encourage you to submit an original research article. If you are interested in submitting a review-type article, please contact the Editorial Office at materialshorizons-rsc@rsc.org in the first instance with a proposed title and abstract, as initial approval is required before submission to avoid topic overlap and ensure that we cover topics in need to review.
When ready please submit your manuscript directly to the submissions platform for Nanoscale Horizons or Materials Horizons where our Editors will assess as per the scope and standards of the journal. Please add a note in the ‘Comments to the Editor’ and ‘Themed issues’ sections of the submission that this is a submission to the ‘Soft wearable sensors’ themed collection in response to the Open Call. Please note that all submissions will be subject to our standard rigorous peer review process, including initial editorial assessment as to suitability for the journal and maintain before peer review, if found appropriate. If accepted, your article would be published in a usual issue of the journal and added to the online collection for extra visibility.
We sincerely hope that you will be able to accept our invitation to contribute to this exciting collection on such an important topic.