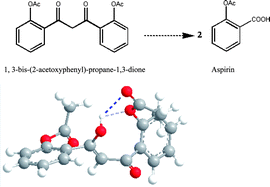
DBMs are β-diketone structural analogues of curcumin and have an aspirin-like skeleton. Curcumin and aspirin are known to possess anti-inflammatory and chemopreventive effects through suppression of COX-2 gene expression. Due to the structural similarities between DBM and curcumin and aspirin, Chuan-Chuan Lin and co-workers tested the anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects of DBMs. They found DBMs to have the potential to substitute for aspirin in therapeutic anti-inflammation treatment. In addition, they also noted the DBMs activities as an anticancer agent.
The team from the China University of Science and Technology and the State University of New Jersey in the US believes that DMBs acts by inhibiting the COX-2 enzyme. It is known that expression of COX-2 is associated with chronic inflammation and epithelial carcinogenesis. The team used the tumour promoting agent 2-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), which induces COX-2 expression causing tumours and ear edema in the skin of mice. Lin et al. found that DBMs inhibited TPA-induced skin tumours significantly and that some of the DMB compounds possessed superior anti-inflammatory properties than aspirin.
Read more about this paper here:
Inhibitory effects of 1,3-bis-(2-substituted-phenyl)-propane-1,3-dione, β-diketone structural analogues of curcumin, on chemical-induced tumor promotion and inflammation in mouse skin
Chuan-Chuan Lin, Yue Liu, Chi-Tang Ho and Mou-Tuan Huang
Food Funct., 2011, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C0FO00098A, Paper