Energy & Environmental Science Perspective
This ‘HOT’ feature article reviews the potential of urea ((NH2)2CO) as a hydrogen carrier for fuel cells and the feasibility of utilising the enormous natural resource of urea that already exists.
Urea is a cheap and readily available resource, and has the advantage over other chemicals of being non-toxic and stable, and therefore easy to transport and store.
The authors say that urea “could be a solution to long-term future sustainable hydrogen supply” and conclude that urea is a realistic sustainable route and could be exploited if sufficient research is undertaken.
Read this ‘HOT’ Perspective today:
Urea as a hydrogen carrier: a perspective on its potential for safe, sustainable and long-term energy supply
Andrew N. Rollinson, Jenny Jones, Valerie Dupont and Martyn V. Twigg
Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C0EE00705F










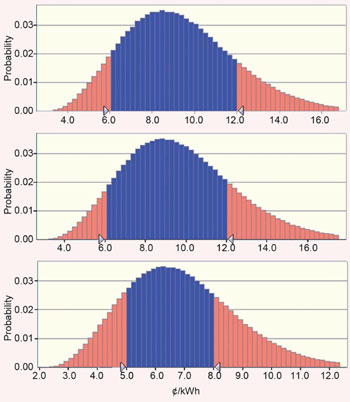


 With increasing pressure on non-renewable energy and chemical sources due to the Earth’s swelling population and dwindling supplies, research into renewable and environmentally friendly feedstocks is of critical importance. In this Energy and Environmental Science review, the authors Tadesse and Luque set out the current state of affairs in an area of research which sits at the interface of two important areas of science: ionic liquids and biofuels.
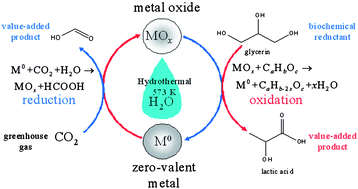
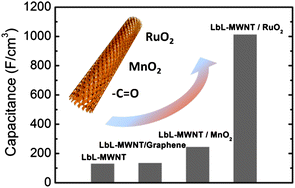
With increasing pressure on non-renewable energy and chemical sources due to the Earth’s swelling population and dwindling supplies, research into renewable and environmentally friendly feedstocks is of critical importance. In this Energy and Environmental Science review, the authors Tadesse and Luque set out the current state of affairs in an area of research which sits at the interface of two important areas of science: ionic liquids and biofuels. Lithium-sulfur batteries are promising rechargeable batteries because of their high energy storage capacity and low cost, but their use has been hindered by their short life cycle and loss of active sulfur through electrochemical reactions in the battery. Porous carbon materials can help as the sulfur is trapped in the pores, preventing it reacting further, but their preparation involves many synthetic steps.
Lithium-sulfur batteries are promising rechargeable batteries because of their high energy storage capacity and low cost, but their use has been hindered by their short life cycle and loss of active sulfur through electrochemical reactions in the battery. Porous carbon materials can help as the sulfur is trapped in the pores, preventing it reacting further, but their preparation involves many synthetic steps.