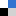Using a combined temperature-vacuum swing (TVS) process which separates CO2 from atmospheric air, scientists from Switzerland have shown a stable performance over 40 consecutive adsorption/desorption cycles.
The adsorption/desorption cycles use a sorbent material made of diamine-functionalized commercial silica gel, and are performed under equilibrium and non-equilibrium (short-cycle) conditions. Therefore the CO2 capture capacity of the material can be determined over a wide range of pressures and temperatures.
Read this ‘HOT’ Energy & Environmental Science article today:
Separation of CO2 from air by temperature-vacuum swing adsorption using diamine-functionalized silica gel
Jan Andre Wurzbacher, Christoph Gebald and Aldo Steinfeld
Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C1EE01681D