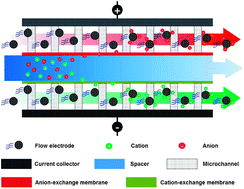
Scientists from Korea present a major step forward in the field of capacitive deionization (CDI) in their recent EES Communication. They cleverly substituted the fixed carbon electrodes used in typical CDI processes with a suspension of active carbon nanoparticles, achieving excellent desalination efficiency.
CDI is a promising water-treatment method. It has the advantage of being more energy efficient that other processes, such as reverse osmosis. However, CDI is not traditionally used for the desalination of salty water, because it requires a discharging step. After the adsorption of a certain amount of ions on the carbon electrodes in the CDI cell, the cell voltage is reduced and the electrodes are shortcircuited. The new method presented in this Communication avoids the need for a discharging step, and therefore allows easy scale-up by simply increasing the number of flow-electrodes used.
Read this HOT Communication today:
Desalination via a new membrane capacitive deionization process utilizing flow-electrodes
Sung-il Jeon, Hong-ran Park, Jeong-gu Yeo, SeungCheol Yang, Churl Hee Cho, Moon Hee Han and Dong Kook Kim
DOI: 10.1039/C3EE24443A