This month sees the following articles in Dalton Transactions that are in the top ten most accessed:-
Recent progress in the synthesis of inorganic nanoparticles
C. N. R. Rao , H. S. S. Ramakrishna Matte , Rakesh Voggu and A. Govindaraj
Dalton Trans., 2012,41, 5089-5120 DOI: 10.1039/C2DT12266A
Naphthylhydrazone based selective and sensitive chemosensors for Cu2+ and their application in bioimaging
Sellamuthu Anbu , Sankarasekaran Shanmugaraju , Rajendran Ravishankaran , Anjali A. Karande and Partha Sarathi Mukherjee
Dalton Trans., 2012,41, 13330-13337 DOI: 10.1039/C2DT31335A
Chelating Schiff base assisted azide-bridged Mn(ii), Ni(ii) and Cu(ii) magnetic coordination polymers
Shi-Qiang Bai , Chen-Jie Fang , Zheng He , En-Qing Gao , Chun-Hua Yan and T. S. Andy Hor
Dalton Trans., 2012,41, 13379-13387 DOI: 10.1039/C2DT31186K
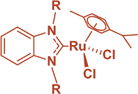
Synthesis of iridium and ruthenium complexes with (N,N), (N,O) and (O,O) coordinating bidentate ligands as potential anti-cancer agents
Stephanie J. Lucas , Rianne M. Lord , Rachel L. Wilson , Roger M. Phillips , Visuvanathar Sridharan and Patrick C. McGowan
Dalton Trans., 2012,41, 13264-13266 DOI: 10.1039/C2DT32104A
Investigation of post-grafted groups of a porous coordination polymer and its proton conduction behavior
Munehiro Inukai , Satoshi Horike , Daiki Umeyama , Yuh Hijikata and Susumu Kitagawa
Dalton Trans., 2012,41, 13261-13263 DOI: 10.1039/C2DT31836A
Thermally and photo-induced spin crossover behaviour in an Fe(ii) imidazolylimine complex: [FeL3](ClO4)2
John R. Thompson , Rosanna J. Archer , Chris S. Hawes , Alan Ferguson , Alain Wattiaux , Corine Mathonière , Rodolphe Clérac and Paul E. Kruger
Dalton Trans., 2012,41, 12720-12725 DOI: 10.1039/C2DT31776A
Selective and colorimetric fluoride anion chemosensor based on s-tetrazines
Yingjie Zhao , Yongjun Li , Zhihong Qin , Runsheng Jiang , Huibiao Liu and Yuliang Li
Dalton Trans., 2012,41, 13338-13342 DOI: 10.1039/C2DT31641B
A small-molecular europium complex with anion sensing sensitivity
Jianwei Wang , Jiang Wu , Yanmei Chen , Haiping Wang , Yiran Li , Weisheng Liu , Hao Tian , Ting Zhang , Jun Xu and Yu Tang
Dalton Trans., 2012,41, 12936-12941 DOI: 10.1039/C2DT31607B
Lanthanides in molecular magnetism: so fascinating, so challenging
Javier Luzon and Roberta Sessoli
Dalton Trans., 2012,41, 13556-13567 DOI: 10.1039/C2DT31388J
Assessing the ligand properties of 1,3-dimesitylbenzimidazol-2-ylidene in ruthenium-catalyzed olefin metathesis
Yannick Borguet , Guillermo Zaragoza , Albert Demonceau and Lionel Delaude
Dalton Trans., 2013, Advance Article DOI: 10.1039/C2DT31520C
Why not take a look at the articles today and blog your thoughts and comments below.
Fancy submitting an article to Dalton Transactions? Then why not submit to us today or alternatively email us your suggestions.