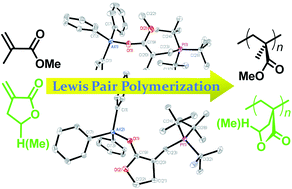
Read more about the polymerization mechanism for FREE for 4 weeks at:
Lewis pair polymerization by classical and frustrated Lewis pairs: acid, base and monomer scope and polymerization mechanism
Yuetao Zhang, Garret M. Miyake, Mallory G. John, Laura Falivene, Lucia Caporaso, Luigi Cavallo and Eugene Y.-X. Chen
Dalton Trans., 2012, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C2DT30427A
This article will form part of a themed issue on Frustrated Lewis Pairs guest edited by Douglas W. Stephan. Other papers in this issue include:
Exchange chemistry of tBu3P(CO2)B(C6F5)2Cl
Rebecca C. Neu, Gabriel Ménard and Douglas W. Stephan
Fixation of carbon dioxide and related small molecules by a bifunctional frustrated pyrazolylborane Lewis pair
Eileen Theuergarten, Janin Schlösser, Danny Schlüns, Matthias Freytag, Constantin G. Daniliuc, Peter G. Jones and Matthias Tamm
[2.2]Paracyclophane derived bisphosphines for the activation of hydrogen by FLPs: application in domino hydrosilylation/hydrogenation of enones
Lutz Greb, Pascual Oña-Burgos, Adam Kubas, Florian C. Falk, Frank Breher, Karin Fink and Jan Paradies












![A Sr2+ salt of [MoVI72MoV60O372(CH3COO)30(H2O)72]42− exhibits a superposed kagome-lattice with huge channels whose diameters measure approximately 3.0 nm A Sr2+ salt of [MoVI72MoV60O372(CH3COO)30(H2O)72]42− exhibits a superposed kagome-lattice with huge channels whose diameters measure approximately 3.0 nm](https://blogs.rsc.org/dt/files/2012/05/GA2.jpg)