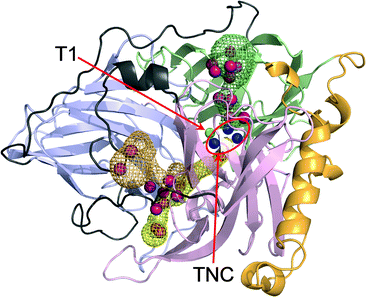
 Christopher F. Blanford’s group from the University of Oxford have solved the x-ray structure for bilirubin oxidase from the plant pathogen Myrothecium verrucaria. This enzyme efficiently catalyses the oxidation of bilirubin to biliverdin, and can be used in O2 reduction.
Christopher F. Blanford’s group from the University of Oxford have solved the x-ray structure for bilirubin oxidase from the plant pathogen Myrothecium verrucaria. This enzyme efficiently catalyses the oxidation of bilirubin to biliverdin, and can be used in O2 reduction.
The authors look at the environment of the copper in the enzyme, to better understand and improve its stability when is attached to the carbon surface of a pyrolytic graphite electrode. When attached to an electrode it can act as a cathode catalyst, and this enhanced electrocatalytic response of the material is an important step in developing viable low-temperature bio-fuel cells.
Read the full article for FREE to find out more about bilirubin oxidase…
Bilirubin oxidase from Myrothecium verrucaria: X-ray determination of the complete crystal structure and a rational surface modification for enhanced electrocatalytic O2 reduction
James A. Cracknell, Thomas P. McNamara, Edward D. Lowe and Christopher F. Blanford
Dalton Trans., 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C0DT01403F










 This Dalton Transactions Hot article explores metalloligands inspired by the active site of enzymes.
This Dalton Transactions Hot article explores metalloligands inspired by the active site of enzymes.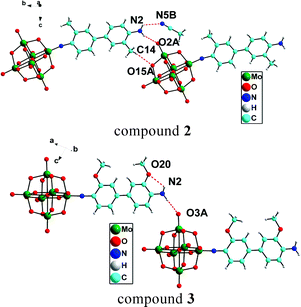
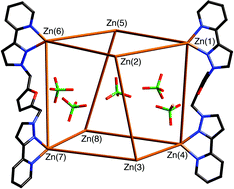 This Dalton Transactions Hot article looks at the self assembly of polyhedral cages.
This Dalton Transactions Hot article looks at the self assembly of polyhedral cages.
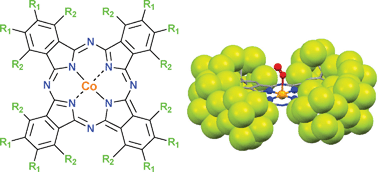 The recently published work of New Jersey Institute of Technology scientists in Dalton Transactions has been picked up by the website
The recently published work of New Jersey Institute of Technology scientists in Dalton Transactions has been picked up by the website 

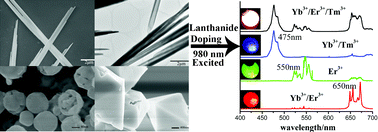 Lanthanide doped Y6O5F8/YF3 microcrystals: phase-tunable synthesis and bright white upconversion photoluminescence properties
Lanthanide doped Y6O5F8/YF3 microcrystals: phase-tunable synthesis and bright white upconversion photoluminescence properties aping Zhang (RSC Publishing Editor) are on a tour of China where they will visit seven universities/institutes and four companies in Beijing, Changchun, Shanghai and Xiamen.
aping Zhang (RSC Publishing Editor) are on a tour of China where they will visit seven universities/institutes and four companies in Beijing, Changchun, Shanghai and Xiamen.![[CuII(Me6TREN)X][X] (X = Br- and Cl-)](https://blogs.rsc.org/dt/files/2011/03/c1dt10189g-ga.gif)