Inorganic materials and nanoparticles are being applied to many of the most pressing challenges facing humanity in the 21st century. They are currently being investigated for their applications in batteries, solar cells, photocatalysts for water splitting and pollutant degradation, and medical theragnostics. Here are some of the most impactful papers in solid state inorganic chemistry from Dalton Transactions in 2017.
Most Downloaded Reviews:
These Frontier and Perspective articles are receiving a lot of attention online, reviewing the advances and trends that are making waves in the solid-state inorganic chemistry community.
Thioborates: potential nonlinear optical materials with rich structural chemistry
Yu-kun Lian, Li-Ming Wu and Ling Chen
Tomokazu Umeyama and Hiroshi Imahori
Yanmei Shi and Bin Zhang
Most Cited Articles:
This original research is off to a great start, as some of our most cited work these papers and communications are already being recognized by the nanomaterials and solid-state chemistry community.
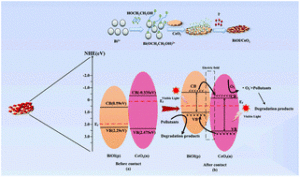
Xiao-Ju Wen, Cheng-Gang Niu, Lei Zhang and Guang-Ming Zeng
| Dalton Trans., 2017, 46, 4982-4993
DOI: 10.1039/C7DT00106A
A novel BiOI/CeO2 photocatalyst with high photocatalytic performance was successfully synthesized via a facile in situ precipitation method. The enhanced photocatalytic performance is ascribed to the formation of a p–n junction, which promotes carrier separation. |
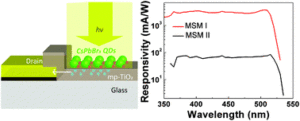
Lin Zhou, Kai Yu, Fan Yang, Jun Zheng, Yuhua Zuo, Chuanbo Li, Buwen Cheng and Qiming Wang
| Dalton Trans., 2017, 46, 1766-1769
DOI: 10.1039/C6DT04758K
Herein, we evaluated an all-inorganic perovskite based MSM photodetector employing a bilayer composite film of mp-TiO2 and CsPbBr3 quantum dots as a photosensitizer.
|
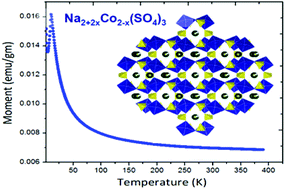
Na2.32Co1.84(SO4)3 as a new member of the alluaudite family of high-voltage sodium battery cathodes
Debasmita Dwibedi, Ritambhara Gond, Allumolu Dayamani, Rafael B. Araujo, Sudip Chakraborty, Rajeev Ahuja and Prabeer Barpanda
| Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 55-63
DOI: 10.1039/C6DT03767D
A novel alluaudite, Na2+2xCo2−x(SO4)3, has been unveiled as a potential high-voltage (ca. 4.8–5.8 V) sodium battery cathode demonstrating antiferromagnetic ordering.
|
Submit your research or reviews on Solid State Inorganic Chemistry and Nanomaterials to Dalton Transactions – see our author guidelines for information on our article types or find out more about the advantages of publishing in a Royal Society of Chemistry journal.