Cyanide compounds can be highly toxic as the cyanide anion inhibits an enzyme in the electron transport chain, cytochrome c oxidase. The inhibition of this enzyme means that cells in the body can no longer produce ATP aerobically for energy which can eventually affect the heart and the central nervous system.
Some industrial processes such as gold mining make use of cyanide ions and the accidental release of these ions can cause serious problems. The potassium salt of cyanide is also used as a terror chemical agent. As such, there is a need for more efficicent detection of cyanide ions with lower detection limits than methods which have been used previously.
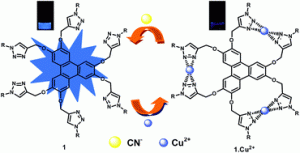 Manoj Kumar and his team at Guru Nanak Dev University, India have synthesized a triazole ( five membered ring with 3 nitrogen and 2 carbon atoms) modified triphenylene (four fused benzene rings) which can selectively complex copper2+ ions.
Manoj Kumar and his team at Guru Nanak Dev University, India have synthesized a triazole ( five membered ring with 3 nitrogen and 2 carbon atoms) modified triphenylene (four fused benzene rings) which can selectively complex copper2+ ions.
The triphenylene based copper ensemble was shown using UV-vis and fluorescence spectroscopy to give a selective response for cyanide ions, even in the presence of blood serum and bovine serum albumin. This paper highlights the potential versatility of the copper ensemble for cyanide detection in different environments.
To read more about the detection of sodium cyanide in tap water and solid state detection of cyanide using the copper ensemble read the full article.
Triphenylene based copper ensemble for the detection of cyanide ions
Vandana Bhalla , Hardev Singh and Manoj Kumar
Dalton Trans., 2012