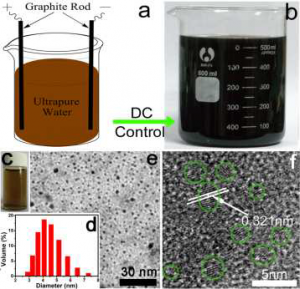
 Quantum dots are nanoparticles of semiconductor material which, because of their very small size, display different optical and electrical properties to that of the corresponding material in the bulk phase. Traditional semiconductor quantum dots are used in optical applications such as cell imaging, LEDs and photodetectors due to their high extinction coefficient.
Quantum dots are nanoparticles of semiconductor material which, because of their very small size, display different optical and electrical properties to that of the corresponding material in the bulk phase. Traditional semiconductor quantum dots are used in optical applications such as cell imaging, LEDs and photodetectors due to their high extinction coefficient.Due to their cheaper cost and intrinsic low toxicity, carbon nanodots (C-dots) have the potential to replace traditional semiconductor quantum dots. To overcome some of the drawbacks with previous methods of fabricating C-dots, Zhenui Kang and his team at Soochow University, China have developed a facile one step electrochemical synthesis. This exciting new method produces c-dots of high purity and uses only pure water as an electrolyte, which is attractive because it is low cost and more environmentally friendly .
The team also synthesized nanohybrid TiO2/C-dots which possess good photocatalytic activity.
To find out more about the photoluminescence and photocatalytic properties of C-dots, read the full Dalton Transactions article…
Large Scale Electrochemical Synthesis of High Quality Carbon Nanodots and Their Photocatalytic Property
Zhenhui Kang, Hai Ming, Zheng Ma, Yang Liu, Keming Pan, Hang Yu and Fang Wang