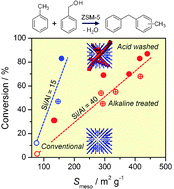
 ZSM-5 is a crystalline zeolite structure used in the petroleum industry as a heterogeneous catalyst for hydrocarbon isomerization reactions. Modification of the microporous structure is being investigated to improve the catalytic potential of the zeolites, alkaline treatment can desilicate the structure and introduce interconnected mesopores. However a consequence of this is the production of extra-framework aluminium and amorphous alumina, which can realuminate on the external surface and affect pore direction.
ZSM-5 is a crystalline zeolite structure used in the petroleum industry as a heterogeneous catalyst for hydrocarbon isomerization reactions. Modification of the microporous structure is being investigated to improve the catalytic potential of the zeolites, alkaline treatment can desilicate the structure and introduce interconnected mesopores. However a consequence of this is the production of extra-framework aluminium and amorphous alumina, which can realuminate on the external surface and affect pore direction.
Acid washing after alkali leaching aims to restore the original framework composition and can enhance the micropore volume, mesoporous surface area, and crystallinity. The effects of these modifications to the ZSM-5 structure undoubtedly affect the catalytic properties as the alkali and acid treatments alter the porosity and composition of the catalyst.
This Hot article by Javier Perez-Ramirez et al. at ETH Zurich aims to de-couple the effects of porosity and composition using the alkylation of toluene (and cyclohexylbenzene) with benzyl alcohol as a model reaction. Alkaline-treated ZSM-5 zeolites are prepared with and without subsequent acid treatment and their catalytic properties determined, the separate effects of porosity and composition are then examined with some very insightful results.
Decoupling porosity and compositional effects on desilicated ZSM-5 zeolites for optimal alkylation performance
Maria Milina, Sharon Mitchell, Zair Domínguez Trinidad, Danny Verboekend and Javier Pérez-Ramírez
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C2CY00456A
All articles are free to access in Catalysis Science & Technology for the duration of 2012, you can also keep up to date with latest news in catalysis by liking us on facbook, following us on twitter and signing up to our e-alert service.
Other articles which may of interest from the Pérez-Ramírez group include:
Design of hierarchical zeolite catalysts by desilication
Danny Verboekend and Javier Pérez-Ramírez
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2011, 1, 879-890
DOI: 10.1039/C1CY00150G, Minireview
Mesoporous ZSM-22 zeolite obtained by desilication: peculiarities associated with crystal morphology and aluminium distribution
Danny Verboekend, André M. Chabaneix, Karine Thomas, Jean-Pierre Gilson and Javier Pérez-Ramírez
CrystEngComm, 2011, 13, 3408-3416
DOI: 10.1039/C0CE00966K, Paper
Hierarchical zeolites: enhanced utilisation of microporous crystals in catalysis by advances in materials design
Javier Pérez-Ramírez, Claus H. Christensen, Kresten Egeblad, Christina H. Christensen and Johan C. Groen
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37, 2530-2542
DOI: 10.1039/B809030K, Critical Review
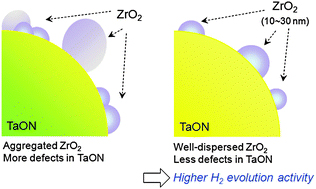












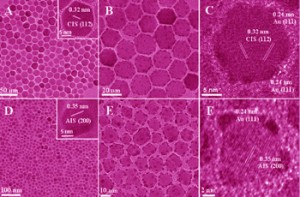
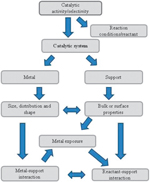

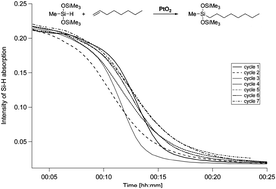 Compared to homogeneous catalysts, heterogeneous catalysts used in hydrosilylation reactions are quite rare. In this HOT article, the catalytic activity and recyclability of PtO2 is examined for the hydrosilylation of n-octene with heptamethyltrisiloxane.
Compared to homogeneous catalysts, heterogeneous catalysts used in hydrosilylation reactions are quite rare. In this HOT article, the catalytic activity and recyclability of PtO2 is examined for the hydrosilylation of n-octene with heptamethyltrisiloxane.