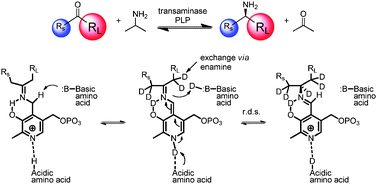
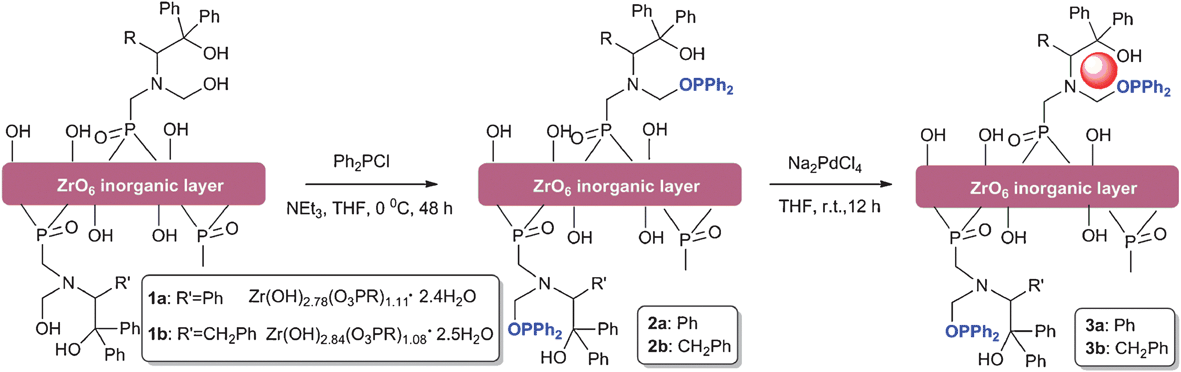
Isotopic labelling is an important tool to investigate chemical processes, from discrete reactions to pharmacodynamics and biological metabolism. Replacing atoms with isotopes is an interesting area of chemistry and this Hot Communication by Matthew Truppo et al. from Merck is no exception.
The team use transaminases to create chiral amines. The method allows efficient generation of both deuterium and tritium labelled amines and is effective on several ketone substrates, potentially providing a general route to D and T labelled chiral amines for a range of applications.
Asymmetric, biocatalytic labeled compound synthesis using transaminases
Matthew Truppo, Jacob M. Janey, Brendan Grau, Krista Morley, Scott Pollack, Greg Hughes and Ian Davies
This article is due to be published in our upcoming themed issue focusing on biocatalysis, other articles to be included in this special issue include,
Mutational analysis of phenolic acid decarboxylase from Bacillus subtilis (BsPAD), which converts bio-derived phenolic acids to styrene derivatives
Annika Frank, William Eborall, Ralph Hyde, Sam Hart, Johan P. Turkenburg and Gideon Grogan
Stereoselective synthesis of bulky 1,2-diols with alcohol dehydrogenases
Justyna Kulig, Robert Christian Simon, Christopher Rose, Masood Husain, Matthias Häckh, Steffen Lüdeke, Kirsten Zeitler, Wolfgang Kroutil, M Pohl and Dörte Rother
Asymmetric reduction of a key intermediate of eslicarbazepine acetate using whole cell biotransformation in a biphasic medium
Manpreet Singh, Sawraj Singh, Sateesh Deshaboina, Hare Krishnen, Richard Lloyd, Karen Holt-Tiffin, Apurba Bhattacharya and Rakeshwar Bandichhor
C2CY00537A