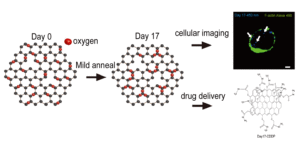
Graphene oxide (GO) has actively been used in various biomedical applications, including biomedical sensors, electronic sensors, functional composites and so on. In addition to having a large surface area, large-scale manufacturability and being dispersible in water, GO shows strong fluorescence and conjugation properties, owing to the abundance of oxygen functional groups on its surface.
Numerous methods have been developed to enable photon emission from GO sheets, such as reduction, labeling with fluorescent protein, and cleaving GO sheets into smaller fragments to produce graphene quantum dots (QDs), although this method does remove oxygen from the carbon lattice. This is a problem because reducing the oxygen content prevents the further functionalization of GO structures with biomolecules. Furthermore, such methods have been reported to cause cytotoxicity.
In this work by the Chen and co-workers, a blue fluorescence was induced in a GO suspension by triggering a phase transformation in GO through treatment with a simple, one-step mild annealing. Previously, it had been difficult to facilitate light emission from GO while preserving the oxygen content and maintaining low cytotoxicity. However, this work suggests that by providing a nano-bio interface for reactions with biomolecules the physical difficulties can be overcome. In this case, GO acts as a bio-imaging agent as well as a functionalization platform for biomolecules. Material characterization and biocompatibility tests were performed to examine the purity, inherent property and non-toxicity of the system. The mechanism for enhanced blue fluorescence upon mild annealing was discovered and modeled through atomistic simulations. Most importantly, GO shows an appealing capability in drug delivery and cellular imaging simultaneously. Overall, this method is expected to be inexpensive, rapid and straightforward, thus holding promise for the development of a whole new class of GO-based nanomaterials for cancer theranostics application in near future.
This article is free to read until 30 May
Simultaneous drug delivery and cellular imaging using graphene oxide, Biomater. Sci., 2018, 6, 813-819
About the webwriter
 Dr. Sudip Mukherjee is a Web Writer for Biomaterials Science. He is currently a Postdoctoral Research Associate at the Rice University. His research is involved in the development of advanced nanomaterials for drug/gene delivery in cancer theranostics, immunomodulatory applications & angiogenesis. He published a total of ~30 research articles/patents. He serves as International Advisory Board Member for ‘Materials Research Express‘, IOP Sciences. He is an associate member (AMRSC) of RSC, UK. He serves as reviewer for several international journals like Chem Comm, J Mater Chem A, J Mater Chem B, Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, RSC Advances, IOP Nanotechnology etc.
Dr. Sudip Mukherjee is a Web Writer for Biomaterials Science. He is currently a Postdoctoral Research Associate at the Rice University. His research is involved in the development of advanced nanomaterials for drug/gene delivery in cancer theranostics, immunomodulatory applications & angiogenesis. He published a total of ~30 research articles/patents. He serves as International Advisory Board Member for ‘Materials Research Express‘, IOP Sciences. He is an associate member (AMRSC) of RSC, UK. He serves as reviewer for several international journals like Chem Comm, J Mater Chem A, J Mater Chem B, Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, RSC Advances, IOP Nanotechnology etc.
Contact Email: sudip.mukherjee@rice.edu
Twitter: https://twitter.com/sudip_88