Suwan Jayasinghe, Analyst, 2013, 138, 2215-2223
The Issue 8 of Analyst is now online. Take a look at our beautiful covers and discover all about the latest research in the field of analytical chemistry.
The outside front cover introduces the interesting minireview written by Suwan Jayasinghe from the University College London, featuring the most recent tools developed to generate fibers, scaffolds and membranes for application in regenerative biology and medicine. According to the author, these structures have important implications in both the laboratory and clinical settings, as they mimic the native extracellular matrix and can be used to directly reconstruct a three-dimensional functional tissue.
Cell electrospinning: a novel tool for functionalising fibres, scaffolds and membranes with living cells and other advanced materials for regenerative biology and medicine
Suwan N. Jayasinghe
Analyst, 2013,138, 2215-2223
DOI: 10.1039/C3AN36599A
Chen at al., Analyst, 2013, 138, 2392-2397
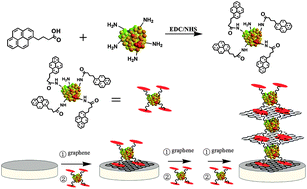
Our inside front cover features the work of Zhong-Ping Yao and colleagues from the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, who reported a new tool for detection and quantitation of ketamine and norketamine. In this study, drugs are detected in urine and oral fluids using wooden-tip electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (WT-ESI-MS). Compared to other methods, this approach has the advantage of little sample preparation and no chromatographic separation.
Rapid detection and quantitation of ketamine and norketamine in urine and oral fluid by wooden-tip electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
Pui-Kin So , Tsz-Tsun Ng , Haixing Wang , Bin Hu and Zhong-Ping Yao
Analyst, 2013,138, 2239-2243
DOI: 10.1039/C3AN36641C
Along with our two new covers, we have some HOT articles for you to enjoy. To know more, click on the links below. All these papers will be free to read until April 4th.
Near-infrared to near-infrared upconverting NaYF4:Yb3+,Tm3+ nanoparticles-aptamer-Au nanorods light resonance energy transfer system for the detection of mercuric(II) ions in solution
Hong-Qi Chen , Fei Yuan , Shao-Zhen Wang , Juan Xu , Yi-Yan Zhang and Lun Wang
Analyst, 2013,138, 2392-2397
DOI: 10.1039/C3AN36921H
Determination of nitrite and glucose in water and human urine with light-up chromogenic response based on the expeditious oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine by peroxynitrous acid
Jia Zhang , Cheng Yang , Chuanxia Chen and Xiurong Yang
Analyst, 2013,138, 2398-2404
DOI: 10.1039/C3AN00080J
Corona discharge radical emission spectroscopy: a multi-channel detector with nose-type function for discrimination analysis
Yunfei Tian , Peng Wu , Xi Wu , Xiaoming Jiang , Kailai Xu and Xiandeng Hou
Analyst, 2013,138, 2249-2253
DOI: 10.1039/C3AN36859A
Reversible binding and quantification of heparin and chondroitin sulfate in water using redox-stable biferrocenylene SAMs
Kun Chen and Michael Schmittel
Analyst, 2013,138, 2405-2410
DOI: 10.1039/C3AN36781A
Comments Off on Analyst Issue 8 now online!