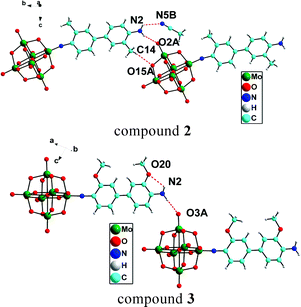
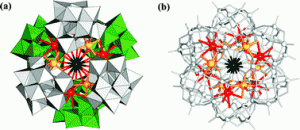
 In this Dalton Transactions Hot Article, En-Bo Wang and colleagues synthesised two nanosized, hexameric POM-based solid assemblies, decorated with six 3d–4f heterometallic clusters: (H2en)6Na15K9[Dy6Fe6(H2O)12(SiW10O38)6]·34H2O and K13Na17[H2en]3[Tb6Fe6-(H2O)12(SiW10O38)6]·40H2O.
In this Dalton Transactions Hot Article, En-Bo Wang and colleagues synthesised two nanosized, hexameric POM-based solid assemblies, decorated with six 3d–4f heterometallic clusters: (H2en)6Na15K9[Dy6Fe6(H2O)12(SiW10O38)6]·34H2O and K13Na17[H2en]3[Tb6Fe6-(H2O)12(SiW10O38)6]·40H2O.
The assemblies were synthesised by a hydrothermal method and characterised by IR, elemental analyses, magnetic studies and single crystal X-ray analysis. The use of organic ligands, pH and reaction temperature all play an important role in the synthesis. The magnetic studies suggest the presence of antiferromagnetic interactions in both compounds.
Read more for FREE until 22nd June 2011:
Hexameric polyoxometalates decorated by six 3d–4f heterometallic clusters
Zhi-Ming Zhang, Yang-Guang Li, Shuang Yao and En-Bo Wang
Dalton Trans., 2011, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C1DT10133A, Paper










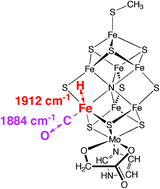 In this HOT article, Ian Dance examines afresh the relationships between CO and H on nitrogenase cofactors following the recent finding that vanadium nitrogenase and modified molybdenum nitrogenase reduce CO to hydrocarbons. In order to assist the interpretation of kinetic infrared spectral data, vibrational frequencies and modes have been calculated for a variety of possible structures in which FeMo-co bears H atoms, or CO ligands, or both.
In this HOT article, Ian Dance examines afresh the relationships between CO and H on nitrogenase cofactors following the recent finding that vanadium nitrogenase and modified molybdenum nitrogenase reduce CO to hydrocarbons. In order to assist the interpretation of kinetic infrared spectral data, vibrational frequencies and modes have been calculated for a variety of possible structures in which FeMo-co bears H atoms, or CO ligands, or both.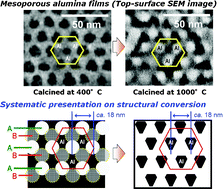 In this HOT article, Wu and Yamauchi et al., reported the synthesis of highly ordered mesoporous alumina thin films existing both as P63/mmc and Fm-3m mesostructures by using triblock copolymer Pluronic P123 as a structure-directing agent and their framework crystallization to γ-alumina phase at 1000 °C. During the crystallization process, large uniaxial shrinkage occurred along the direction perpendicular to the substrate with the retention of horizontal mesoscale periodicity, thereby forming vertically oriented nanopillars on the film surface.
In this HOT article, Wu and Yamauchi et al., reported the synthesis of highly ordered mesoporous alumina thin films existing both as P63/mmc and Fm-3m mesostructures by using triblock copolymer Pluronic P123 as a structure-directing agent and their framework crystallization to γ-alumina phase at 1000 °C. During the crystallization process, large uniaxial shrinkage occurred along the direction perpendicular to the substrate with the retention of horizontal mesoscale periodicity, thereby forming vertically oriented nanopillars on the film surface.


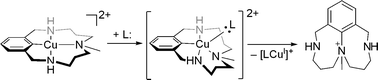
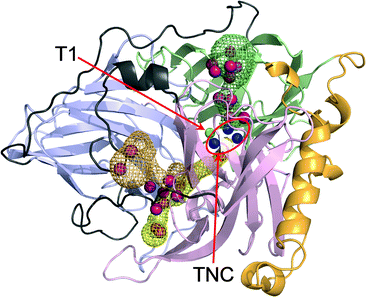
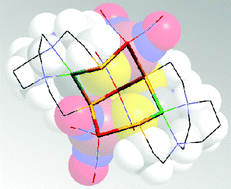 This Dalton Transactions Hot article explores metalloligands inspired by the active site of enzymes.
This Dalton Transactions Hot article explores metalloligands inspired by the active site of enzymes.