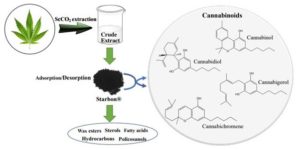
There are a number of natural product extracts that contain pharmaceutically active ingredients or APIs. These APIs are extracted alongside a host of other compounds such as terpenes, fatty acids, sterols and waxes that naturally occur within the plant. A very topical example are the family of cannabinoids found in hemp extract. Isolating these cannabinoids is a multi-step, energy and solvent intensive process.
Recent work at the Green Chemistry Centre of Excellence, University of York, has shown that mesoporous materials made from naturally derived alginic acid, known as Starbons, work incredibly well at isolating cannabinoids in a single step. Here the Starbon is used in solid phase extraction (SPE) to purify a host of cannabinoids by solvent selection (Figure 1).
Starbons are able to act in highly selective SPE for two reasons, the first being that their mesopores are large enough (2-50 nm) for complex compounds to enter and leave. The second is the temperature at which they are pyrolysed allows tuning of surface chemistry from hydrophilic to hydrophobic. By screen Starbons produced at 300, 450 and 800 °C, adsorption and desorption solvents (hexane and ethanol respectively) and contact time (30 seconds), we were able to isolate 93% of cannabinoids (by GC-FID) from the extract in a single step (Figure 2). The process was also validated using in line extraction and isolation in supercritical carbon dioxide, where the feedstock was hemp dust. This was especially interesting as the cannabinoid content in this industrial by-product is significantly lower than in hemp top flowers.

Figure 2 – GCchromatograph of hemptops; Crude C. sativa extract, Desorption phase (ethanol)after passing through A300.
Corresponding Author:
Dr Con Robert McElroy (Rob) is a senior researcher at the Green Chemistry Centre of Excellence, Department of Chemistry, University of York. Rob gained his Ph.D in 2007 at Keele University working on the production of composite materials from copolymers incorporating renewable resources. He was a postdoc working on carbonate chemistry for two years at Ca Foscari University of Venice and joined the Green Chemistry Centre of Excellence, University of York as a PDRA in 2011. His current role is as Deputy Director of the Circa Renewable Carbon Institute which focuses on reactions and/or applications of levoglucosenone and the bio-derived solvent Cyrene (developed at the University of York and which he is a co-inventor of). He has published 3 book chapters, 39 papers, 4 reviews and 3 patents and has a H index of 20.
In 2019 he became chief technical officer of Starbons Ltd in which time it has become revenue generating, award winning and has won funding/made sales in relation to projects he managed.
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Con-Mcelroy