RSC Pharmaceutics has published its first articles. To celebrate this, we asked the authors to discuss their work in some more detail.
In this edition, we hear from Shanka Walia and Mohit J. Mehta about their study titled “Recent Progress on Nanosystems for Nucleic Acid Delivery.”
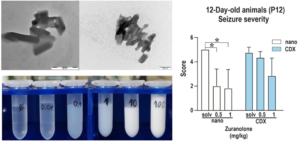
“The review provides a comprehensive overview of the use of nanocarriers for the delivery of nucleic acid-based therapeutics. We have discussed the challenges associated with the delivery of nucleic acids, such as their instability, degradation, and inefficient delivery to target cells. The review not only highlights these challenges but also presents a beacon of hope in the form of the potential of lipid-based delivery systems to overcome them. We have discussed various types of lipid-based nanocarriers, including cationic lipids, ionizable lipids, zwitterionic lipids, lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), liposomes, and solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs). The review also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each type of nanocarrier. Finally, we have concluded the review by emphasizing the potential of lipid-based nanocarriers to revolutionize the field of nucleic acid therapeutics, inspiring a sense of optimism and anticipation among our readers.
The most exciting aspect of this research is the potential of lipid-based nanocarriers to revolutionize the field of nucleic acid therapeutics. This potential is not just promising, but it’s a game-changer. We have highlighted the many advantages of these nanocarriers, such as their ability to protect nucleic acids from degradation, enhance their cellular uptake, and target them to specific cells and tissues. We have also discussed the recent successes of lipid-based nanocarriers in developing mRNA vaccines for COVID-19. The potential impact of this work is significant. Lipid-based nanocarriers have the potential to enable the development of new and more effective treatments for various diseases, including cancer, genetic disorders, and infectious diseases. Our review provides a valuable overview of the current state of the field. It highlights the challenges that need to be overcome to fully realize the potential of lipid-based nanocarriers.”
Want to know more about their work? Read the full paper here!
Recent progress on Nanosystems for Nucleic Acid Delivery
Shanka Walia and Mohit J. Mehta
RSC Pharm. 2024, Advance Article, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4PM00009A
 |
RSC Pharmaceutics provides researchers with a platform to publish research in pharmaceutics and advance this field. We are interested in any submission that shares new scientific findings across chemistry, materials science, biomedical sciences, pharmaceutics and drug delivery.
|