Below you can find the top 25 most-read Nanoscale articles from the whole of 2012, including reviews and original research across the fields of nanoscience and nanotechnology.
Below you can find the top 25 most-read Nanoscale articles from the whole of 2012, including reviews and original research across the fields of nanoscience and nanotechnology.
Nanoscale publishes work of the highest quality and impact, is fully-indexed in ISI, MEDLINE and all other leading databases and its Impact Factor is currently 5.9.
Our free table-of-contents e-alert allows you to keep up to date with each issue as it is published.
We invite you to submit your best research to Nanoscale in 2013.
Top 25 most-read Nanoscale articles for 2012
Graphene edges: a review of their fabrication and characterization
Xiaoting Jia, Jessica Campos-Delgado, Mauricio Terrones, Vincent Meunier and Mildred S. Dresselhaus
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00600A
Gold nanoparticles: preparation, properties, and applications in bionanotechnology
Yi-Cheun Yeh, Brian Creran and Vincent M. Rotello
DOI: 10.1039/C1NR11188D
Nanostructured metal oxide-based materials as advanced anodes for lithium-ion batteries
Hao Bin Wu, Jun Song Chen, Huey Hoon Hng and Xiong Wen (David) Lou
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR11966H
Recent progress on metal core@semiconductor shell nanocomposites as a promising type of photocatalyst
Nan Zhang, Siqi Liu and Yi-Jun Xu
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR00009A
3D branched nanowire heterojunction photoelectrodes for high-efficiency solar water splitting and H2 generation
Ke Sun, Yi Jing, Chun Li, Xiaofeng Zhang, Ryan Aguinaldo, Alireza Kargar, Kristian Madsen, Khaleda Banu, Yuchun Zhou, Yoshio Bando, Zhaowei Liu and Deli Wang
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR11952H
Li ion battery materials with core–shell nanostructures
Liwei Su, Yu Jing and Zhen Zhou
DOI: 10.1039/C1NR10550G
The role of nanomaterials in redox-based supercapacitors for next generation energy storage devices
Xin Zhao, Beatriz Mendoza Sánchez, Peter J. Dobson and Patrick S. Grant
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00594K
Recent advances in solar cells based on one-dimensional nanostructure arrays
Miao Yu, Yun-Ze Long, Bin Sun and Zhiyong Fan
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR30437F
A cuprous oxide–reduced graphene oxide (Cu2O–rGO) composite photocatalyst for hydrogen generation: employing rGO as an electron acceptor to enhance the photocatalytic activity and stability of Cu2O
Phong D. Tran, Sudip K. Batabyal, Stevin S. Pramana, James Barber, Lydia H. Wong and Say Chye Joachim Loo
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR30881A
2D materials: to graphene and beyond
Rubén Mas-Ballesté, Cristina Gómez-Navarro, Julio Gómez-Herrero and Félix Zamora
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00323A
Microwave chemistry for inorganic nanomaterials synthesis
Idalia Bilecka and Markus Niederberger
DOI: 10.1039/B9NR00377K
Preparation, properties and applications of polysaccharide nanocrystals in advanced functional nanomaterials: a review
Ning Lin, Jin Huang and Alain Dufresne
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR30260H
Graphene: nanoscale processing and recent applications
László P. Biró, Péter Nemes-Incze and Philippe Lambin
DOI: 10.1039/C1NR11067E
Recent advances in the efficient reduction of graphene oxide and its application as energy storage electrode materials
Tapas Kuila, Ananta Kumar Mishra, Partha Khanra, Nam Hoon Kim and Joong Hee Lee
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR32703A
Three-dimensional graphene architectures
Chun Li and Gaoquan Shi
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR31467C
Graphene transfer: key for applications
Junmo Kang, Dolly Shin, Sukang Bae and Byung Hee Hong
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR31317K
Multifunctional composite core–shell nanoparticles
Suying Wei, Qiang Wang, Jiahua Zhu, Luyi Sun, Hongfei Lin and Zhanhu Guo
DOI: 10.1039/C1NR11000D
Nanostructured carbon–metal oxide composite electrodes for supercapacitors: a review
Mingjia Zhi, Chengcheng Xiang, Jiangtian Li, Ming Li and Nianqiang Wu
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR32040A
Quantum sized, thiolate-protected gold nanoclusters
Rongchao Jin
DOI: 10.1039/B9NR00160C
TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers
Akira Isogai, Tsuguyuki Saito and Hayaka Fukuzumi
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00583E
Conjugated polymers/semiconductor nanocrystals hybrid materials—preparation, electrical transport properties and applications
Peter Reiss, Elsa Couderc, Julia De Girolamo and Adam Pron
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00403K
Recent progress on graphene-based photocatalysts: current status and future perspectives
Nan Zhang, Yanhui Zhang and Yi-Jun Xu
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR31480K
Mechanised nanoparticles for drug delivery
Karla K. Cotí, Matthew E. Belowich, Monty Liong, Michael W. Ambrogio, Yuen A. Lau, Hussam A. Khatib, Jeffrey I. Zink, Niveen M. Khashab and J. Fraser Stoddart
DOI: 10.1039/B9NR00162J
Theranostic nanoplatforms for simultaneous cancer imaging and therapy: current approaches and future perspectives
Ki Young Choi, Gang Liu, Seulki Lee and Xiaoyuan Chen
DOI: 10.1039/C1NR11277E
6.5% efficient perovskite quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell
Jeong-Hyeok Im, Chang-Ryul Lee, Jin-Wook Lee, Sang-Won Park and Nam-Gyu Park
DOI: 10.1039/C1NR10867K

Comments Off on Nanoscale most-read articles in 2012
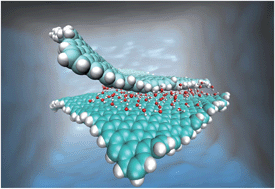










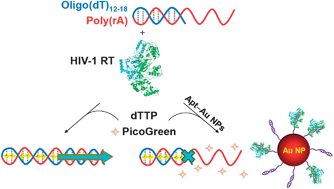 Gold nanoparticles functionalised with aptamers have been found to be highly effective inhibitors for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. The nanoparticles particles have been shown to reduce the ability of the HIV virus to reproduce and infect new cells.
Gold nanoparticles functionalised with aptamers have been found to be highly effective inhibitors for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. The nanoparticles particles have been shown to reduce the ability of the HIV virus to reproduce and infect new cells.



 In this
In this