This month sees the following articles in Nanoscale that are in the top 25 most accessed from April – June:
Nanoelectronic biosensors based on CVD grown graphene
Yinxi Huang, Xiaochen Dong, Yumeng Shi, Chang Ming Li, Lain-Jong Li and Peng Chen
Nanoscale, 2010,2, 1485-1488
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00142B
Glutathione-functionalized graphene quantum dots as selective fluorescent probes for phosphate-containing metabolites
Jing-Jing Liu, Xiao-Long Zhang, Zhong-Xiao Cong, Zhi-Tao Chen, Huang-Hao Yang and Guo-Nan Chen
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 1810-1815
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR33794D
Recent progress on graphene-based photocatalysts: current status and future perspectives
Nan Zhang, Yanhui Zhang and Yi-Jun Xu
Nanoscale, 2012,4, 5792-5813
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR31480K
Recent advances in the efficient reduction of graphene oxide and its application as energy storage electrode materials
Tapas Kuila, Ananta Kumar Mishra, Partha Khanra, Nam Hoon Kim and Joong Hee Lee
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 52-71
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR32703A
Recent progress on metal core@semiconductor shell nanocomposites as a promising type of photocatalyst
Nan Zhang, Siqi Liu and Yi-Jun Xu
Nanoscale, 2012,4, 2227-2238
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR00009A
Surface-functionalized nanoparticles for biosensing and imaging-guided therapeutics
Shan Jiang, Khin Yin Win, Shuhua Liu, Choon Peng Teng, Yuangang Zheng and Ming-Yong Han
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 3127-3148
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR34005H
Environmental applications using graphene composites: water remediation and gas adsorption
K. Christian Kemp, Humaira Seema, Muhammad Saleh, Nhien H. Le, Kandula Mahesh, Vimlesh Chandra and Kwang S. Kim
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 3149-3171
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR33708A
Nanostructured carbon–metal oxide composite electrodes for supercapacitors: a review
Mingjia Zhi, Chengcheng Xiang, Jiangtian Li, Ming Li and Nianqiang Wu
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 72-88
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR32040A
Crystalline structure-dependent growth of bimetallic nanostructures
Qian Li, Ruibin Jiang, Tian Ming, Caihong Fang and Jianfang Wang
Nanoscale, 2012,4, 7070-7077
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR31900D
A review of fabrication and applications of carbon nanotube film-based flexible electronics
Steve Park, Michael Vosguerichian and Zhenan Bao
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 1727-1752
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR33560G
A SnO2@carbon nanocluster anode material with superior cyclability and rate capability for lithium-ion batteries
Min He, Lixia Yuan, Xianluo Hu, Wuxing Zhang, Jie Shu and Yunhui Huang
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 3298-3305
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR34133J
2D materials: to graphene and beyond
Rubén Mas-Ballesté, Cristina Gómez-Navarro, Julio Gómez-Herrero and Félix Zamora
Nanoscale, 2011,3, 20-30
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00323A
Excellent catalytic effects of highly crumpled graphene nanosheets on hydrogenation/dehydrogenation of magnesium hydride
Guang Liu, Yijing Wang, Changchang Xu, Fangyuan Qiu, Cuihua An, Li Li, Lifang Jiao and Huatang Yuan
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 1074-1081
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR33347C
All-solid-state hybrid solar cells based on a new organometal halide perovskite sensitizer and one-dimensional TiO2 nanowire arrays
Jianhang Qiu, Yongcai Qiu, Keyou Yan, Min Zhong, Cheng Mu, He Yan and Shihe Yang
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 3245-3248
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR00218G
Hierarchically plasmonic photocatalysts of Ag/AgCl nanocrystals coupled with single-crystalline WO3 nanoplates
Deliang Chen, Tao Li, Qianqian Chen, Jiabing Gao, Bingbing Fan, Jian Li, Xinjian Li, Rui Zhang, Jing Sun and Lian Gao
Nanoscale, 2012,4, 5431-5439
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR31030A
Zirconium phosphate nanoplatelets: a biocompatible nanomaterial for drug delivery to cancer
Vipin Saxena, Agustin Diaz, Abraham Clearfield, James D. Batteas and Muhammad Delwar Hussain
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 2328-2336
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR34242E
Advances in 2D boron nitride nanostructures: nanosheets, nanoribbons, nanomeshes, and hybrids with graphene
Yi Lin and John W. Connell
Nanoscale, 2012,4, 6908-6939
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR32201C
Nano–bio effects: interaction of nanomaterials with cells
Liang-Chien Cheng, Xiumei Jiang, Jing Wang, Chunying Chen and Ru-Shi Liu
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 3547-3569
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR34276J
Dimension-tailored functional graphene structures for energy conversion and storage
Jing Zhang, Fei Zhao, Zhipan Zhang, Nan Chen and Liangti Qu
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 3112-3126
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR00011G
Graphene synthesis: relationship to applications
Rebecca S. Edwards and Karl S. Coleman
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 38-51
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR32629A
Gram-scale synthesis of ultrasmall SnO2 nanocrystals with an excellent electrochemical performance
Yuejiao Chen, Jianmin Ma, Qiuhong Li and Taihong Wang
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 3262-3265
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR00356F
Graphene-related nanomaterials: tuning properties by functionalization
Qing Tang, Zhen Zhou and Zhongfang Chen
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 4541-4583
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR33218G
Three-dimensional graphene architectures
Chun Li and Gaoquan Shi
Nanoscale, 2012,4, 5549-5563
DOI: 10.1039/C2NR31467C
Gold nanoparticle-enhanced luminescence of silicon quantum dots co-encapsulated in polymer nanoparticles
Noor Aniza Harun, Matthew J. Benning, Benjamin R. Horrocks and David A. Fulton
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 3817-3827
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR00421J
Intracellular cleavable poly(2-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient siRNA delivery in vitro and in vivo
Daoshu Lin, Qiang Cheng, Qian Jiang, Yuanyu Huang, Zheng Yang, Shangcong Han, Yuning Zhao, Shutao Guo, Zicai Liang and Anjie Dong
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 4291-4301
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR00294B
Why not take a look at the articles today and blog your thoughts and comments below.
Fancy submitting an article to Nanoscale? Then why not submit to us today!










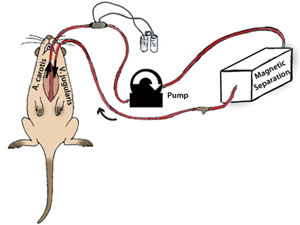
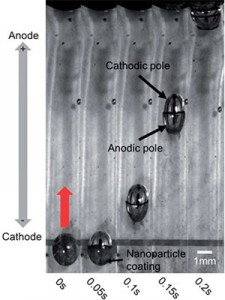
 Seawater can be used as fuel to propel micromotors say scientists in the US.
Seawater can be used as fuel to propel micromotors say scientists in the US.