Huanxin Cai and Ping Yao, from Fudan University, have developed a facile and green approach for the synthesis of gold nanoparticle conjugates prepared from a lys-dex nangel, comprising a lysozyme core with a dextran shell. The Au@lys-dex nangels loaded with doxorubicin show the same antitumour activity as free doxorubicin, showing the potential of the nanogels for drug delivery applications.
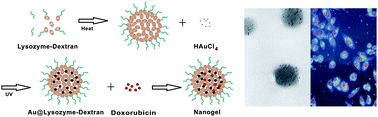
By mixing the lys-dex nanogel and chloroauric acid at pH 4, gold nanoparticles can be synthesized by inducing the reduction of Au3+ using UV photo-irradiation. The synthesis process was monitored by UV-Vis spectroscopy indicating that 2 hours of UV-irradiation is sufficient to produce gold nanoparticles with a surface plasmon band centered at 536 nm. The authors report that the gold nanoparticle morphology can be controlled by altering the pH of the reaction, thereby leading to nanoparticles with sizes of 11, 8 and 4 nm at pH 2, 4 and 6, respectively.
Due to the plasmonic properties of the nanoparticles, the Au@lys-dex nanogels can also be used as contrast agents for optical microscopy imaging. The authors have therefore devised a nanoparticle system for simultaneous drug delivery and biomedical imaging applications.
by Dr Lee Barrett
Read the full details of this HOT Nanoscale paper today:
In situ preparation of gold nanoparticle-loaded lysozyme–dextran nanogels and applications for cell imaging and drug delivery
Huanxin Cai and Ping Yao
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR00178D