Self-Assembly of Aligned Rutile@Anatase TiO2 Nanorod@CdS Quantum Dots Ternary Core-Shell Heterostructure: Cascade Electron-Transfer by Interfacial Design
Fang-Xing Xiao, Jianwei Miao and Bin Liu
 A novel self-assembly approach based on electrostatic interaction has been developed for the synthesis of rutile@anatase TiO2 nanorod (NR)@CdS quantum dots (QDs) ternary core-shell heterostructure, for which in-situ formed monodispersed anatase TiO2 layer was intimately sandwiched between rutile TiO2 NRs and CdS QDs. It has been demonstrated that the well-defined bilayer interface significantly improves the photocatalytic performance of the ternary heterostructure (i.e. rutile@anatase TiO2 NR@CdS QDs), owing predominantly to the appropriate band alignment of constituting semiconductors, thus facilitating photogenerated electron-hole separation and charge collection under simulated solar light irradiation.
A novel self-assembly approach based on electrostatic interaction has been developed for the synthesis of rutile@anatase TiO2 nanorod (NR)@CdS quantum dots (QDs) ternary core-shell heterostructure, for which in-situ formed monodispersed anatase TiO2 layer was intimately sandwiched between rutile TiO2 NRs and CdS QDs. It has been demonstrated that the well-defined bilayer interface significantly improves the photocatalytic performance of the ternary heterostructure (i.e. rutile@anatase TiO2 NR@CdS QDs), owing predominantly to the appropriate band alignment of constituting semiconductors, thus facilitating photogenerated electron-hole separation and charge collection under simulated solar light irradiation.
Mater. Horiz., 2013, DOI: 10.1039/c3mh00097d, Accepted Manuscript
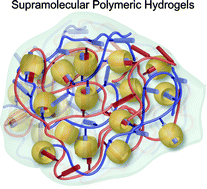
Supramolecular host–guest polymeric materials for biomedical applications
Xian Jun Loh
The bottom–up synthesis of highly complex functional materials from simple modular blocks is an intriguing area of research. Driven by the chemistry of supramolecular assembly, modules which self-assemble into intricate structures have been described. These hierarchically assembled systems extend beyond the individual molecule and rely on non-covalent interactions in a directed self-assembly process. The intrinsic properties of the materials can be modified by exploiting the dynamic and specific uni-directional interactions among the building. This also allows the building of novel supramolecular structures such as hydrogels, micelles and vesicles. These aqueous supramolecular networks belong to a novel category of soft biomaterials exhibiting attractive properties such as stimuli-responsiveness and self-healing properties derived from their dynamic behavior. These are important for a wide variety of emerging applications. In this review, the latest literature describing the formation of dynamic polymeric networks through host–guest complex formation will be summarised. These approaches carried out in the aqueous medium have unlocked a versatile toolbox for the design and fine-tuning of supramolecular self-assembled materials.
Mater. Horiz., 2014, DOI: 10.1039/c3mh00057e, Advanced Article
Protein coronas suppress the hemolytic activity of hydrophilic and hydrophobic nanoparticles
Krishendu Saha, Daniel Moyano and Vincent M Rotello
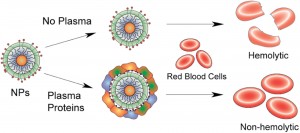 The role of nanoparticle surface hydrophobicity on its hemolytic property is established in the absence and the presence of plasma proteins. Significantly, the formation of plasma protein corona on NP surface protects red blood cells from both hydrophilic and hydrophobic NP-mediated hemolysis.
The role of nanoparticle surface hydrophobicity on its hemolytic property is established in the absence and the presence of plasma proteins. Significantly, the formation of plasma protein corona on NP surface protects red blood cells from both hydrophilic and hydrophobic NP-mediated hemolysis.
Mater. Horiz., 2013, DOI: 10.1039/c3mh00075c, Accepted Manuscript
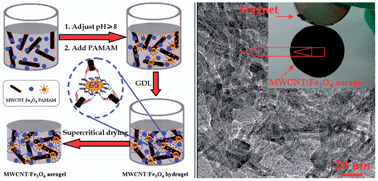
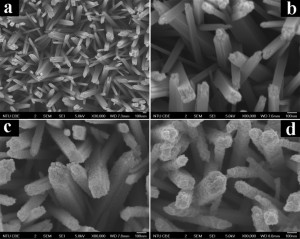
Dendrimer-linked, renewable and magnetic carbon nanotube aerogels
Xuetong Zhang, Liang Chen, Tianyu Yuan, Huan Huang, Zhuyin Sui, Ran Du, Xin Li, Yun Lua and Qingwen Lib
Magnetic carbon nanotube aerogels with a repeated aerogel–sol–hydrogel–aerogel transition have been acquired by the special drying of gel-precursors made via assembling individual nanotubes with dendritic poly(amido amine) molecules in the presence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles, which has inspired us to synthesize renewable 3D porosints composed of organic, inorganic and their hybrid building blocks.
Mater. Horiz., 2014, DOI: 10.1039/c3mh00076a, Advanced Article