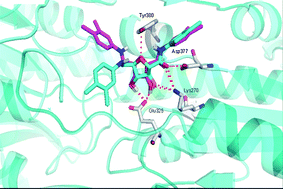
Phosphofructokinase is a kinase enzyme that phosphorylates fructose 6-phosphate in the glycolysis metabolic pathway, and is of central importance to carbohydrate metabolism. As such it is a very promising target for anti-trypanosomal drug design to treat sleeping sickness.
In this review Renata B. Oliveira et al. present a survey of recent literature regarding the structural and functional properties of phosphofructokinase as well as discussing its importance as a target in the development of selective therapeutics to treat Human African trypanosomiasis.
Phosphofructokinase: structural and functional aspects and design of selective inhibitors
Stefânia N. Lavorato, Saulo F. Andrade, Thaïs H. A. Silva, Ricardo J. Alves and Renata B. Oliveira
DOI: 10.1039/C2MD20122D