Determination of Sr to study geological processes
The different isotopes of Strontium (Sr) can provide information on biological, hydrological and geological processes. Measurements of the radiogenic isotopic composition (87Sr/86Sr) have been used for a long time to study these processes, but in the last 30 years the stable isotopic ratio (88Sr/86Sr) has shown potential to help better understand the source of Sr and the cause of mass fractionation, especially when combined with 87Sr/86Sr measurements.
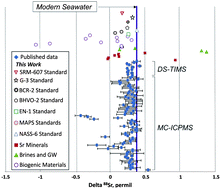
Leonid Neymark and scientists from both the US Geological Survey in Denver and the Instutute of Precambrian Geology and Geochronology of the Russian Academy of Sciences developed a thermal ionisation mass spectrometry (TIMS) method to measure Sr concentration, and “true” 88Sr/86Sr, 87Sr/86Sr and δ88Sr values. “True” values of isotopic ratios are considered those that are caused by natural fractionation, so the values measured have to be corrected for any chemical separation occurring during the measurement. This was achieved by spiking the samples with two Sr isotopes, in this study 87Sr-84Sr, with a precisely known ratio.
Standards, along with fossils, modern fauna, abiogenic minerals, silicate whole rocks and various water samples were analysed and the total range of values of δ88Sr shows potential for δ88Sr to be used as a tracer alongside the 87Sr/86Sr tracer.
To read the full article, please access the link below. This paper will be free to read until 6 january 2014.
Precise determination of δ88Sr in rocks, minerals, and waters by double-spike TIMS: a powerful tool in the study of geological, hydrological and biological processes
Leonid A. Neymark, Wayne R. Premo, Nikolay N. Mel’nikov and Poul Emsbo
J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2014,29, 65-75
DOI: 10.1039/C3JA50310K











 Frank Vanhaecke
Frank Vanhaecke
 Reversible polymerization of novel monomers bearing furan and plant oil moieties: a double click exploitation of renewable resources
Reversible polymerization of novel monomers bearing furan and plant oil moieties: a double click exploitation of renewable resources



 The
The