Scientists from Texas, US, have investigated the effects of limonoids on human breast cancer cells. Limonoids, found in lemons and other citrus fruits such as oranges and grapefruit, have been previously found to exhibit various health benefits such as antitumor , antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory properties. They have also been shown to prevent coronary heart disease. However, the mechanism behind their anticancer activity remains unclear.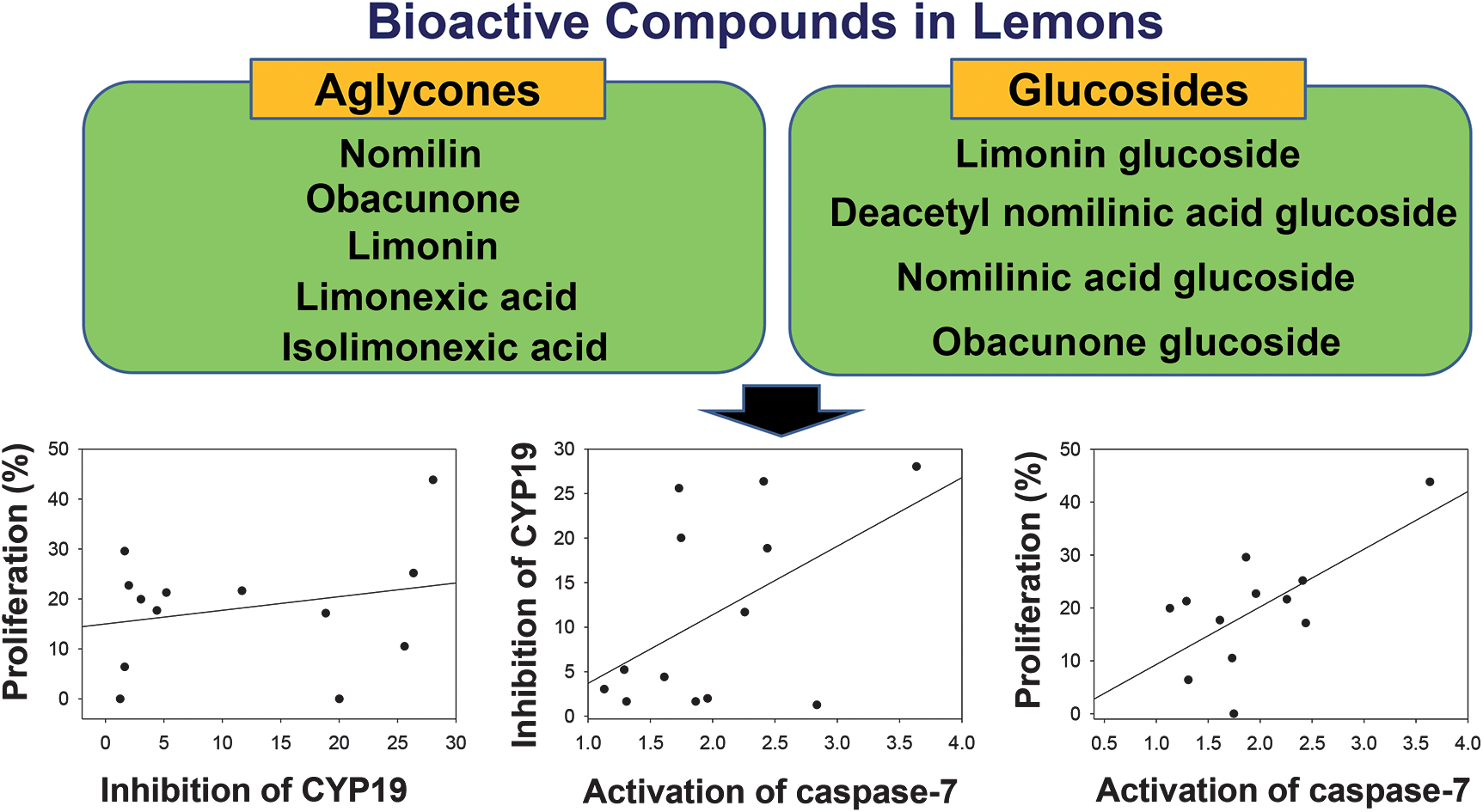
Estrogen is known to affect breast cancer, and the presence estrogen receptors (ER) results in a better prognosis for the patient compared to ER-negative tumors. In this work, the team isolated and identified limonoids from lemon seeds and screened them for cytotoxicity against both ER-negative (MDA-MB-231) and ER-positive (MCF-7) breast cancer cells. Most of the limonoids showed antiaromatase activity, however anti-proliferative activity was significantly correlated with caspase-7 activation by limonoids.
The results show that citrus limonoids may have the potential to prevent estrogen-responsive breast cancer (MCF-7) via caspase-7 dependent pathways.
To read the article in full, please click the link below. Free to access until the 12th December 2012!
Limonoids and their anti-proliferative and anti-aromatase properties in human breast cancer cells, Jinhee Kim, Guddadarangavvanahally K. Jayaprakasha and Bhimanagouda S. Patil, Food Funct., 2013, DOI: 10.1039/c2fo30209h
You can keep up to date with the latest developments from Food & Function by signing up for free table of contents alerts and monthly e-newsletters.