 Rational design of MOFs is a complex task with a range of variables including ligands, metals, reaction conditions and solvents, this HOT Communication in Dalton Trans. details the synthesis of a novel metal organic framework (MOF) using an aromatic linker and CdBr2. Leonard Barbour and Marike du Plessis synthesised the framework with different solvents and discovered different packing modes for the different solvent systems…… to find out more about their discoveries read the full Communication in Dalton Transactions.
Rational design of MOFs is a complex task with a range of variables including ligands, metals, reaction conditions and solvents, this HOT Communication in Dalton Trans. details the synthesis of a novel metal organic framework (MOF) using an aromatic linker and CdBr2. Leonard Barbour and Marike du Plessis synthesised the framework with different solvents and discovered different packing modes for the different solvent systems…… to find out more about their discoveries read the full Communication in Dalton Transactions.
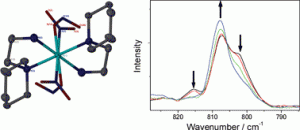
Supramolecular isomerism and solvatomorphism in a novel coordination compound
Marike du Plessis and Leonard J. Barbour
Dalton Trans., 2012, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C1DT11564B, Communication











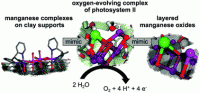
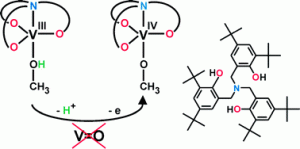
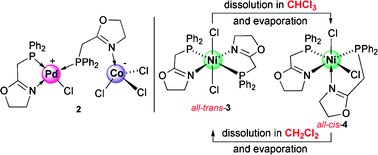 Transition metal complexes bearing functional P,N-type ligands attract much attention because they combine hard nitrogen donor(s) and soft phosphorus donor(s) and offer considerable chemical and structural diversity. In this HOT Article, Braunstein et al. report several palladium/cobalt and nickel complexes with phosphino-oxazoline ligands. Some of the nickel complexes were further checked for their ethylene reactivity, and showed activity for ethylene non-selective oligomerization. Interestingly, a reversible interconversion transform phenomena was observed between a couple of the isomeric Ni-complexes with variation of the solvent between CH2Cl2 and CHCl3.
Transition metal complexes bearing functional P,N-type ligands attract much attention because they combine hard nitrogen donor(s) and soft phosphorus donor(s) and offer considerable chemical and structural diversity. In this HOT Article, Braunstein et al. report several palladium/cobalt and nickel complexes with phosphino-oxazoline ligands. Some of the nickel complexes were further checked for their ethylene reactivity, and showed activity for ethylene non-selective oligomerization. Interestingly, a reversible interconversion transform phenomena was observed between a couple of the isomeric Ni-complexes with variation of the solvent between CH2Cl2 and CHCl3.
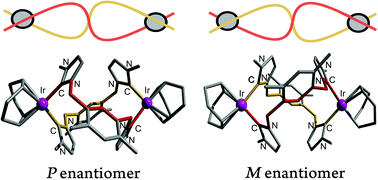 Braunstein and co-workers have formed a dinuclear Ir(I) complex with a bis-NHC ligand in situ from
Braunstein and co-workers have formed a dinuclear Ir(I) complex with a bis-NHC ligand in situ from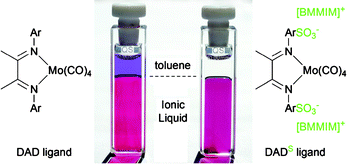 Oelkers and Sundermeyer, in this HOT Article, present a general approach towards 1,4-diazabutadiene (DADS) ligands with various onium cations via acid–base reactions and towards their noble-metal complexes. The solubility and immobilization of such complexes in ILs is quantitatively shown via photometric measurements using a chromophoric Mo(0) DADS complex in a toluene/[BMIM]OTf biphasic mixture as a model system. It was shown that complexes with ionic liquid (IL) – typical onium salts of sulfonated diazadienes as ligands are strongly retained in an IL phase in contact with a toluene phase, which may make these ligands potentially useful in IL/organic biphasic catalysis.
Oelkers and Sundermeyer, in this HOT Article, present a general approach towards 1,4-diazabutadiene (DADS) ligands with various onium cations via acid–base reactions and towards their noble-metal complexes. The solubility and immobilization of such complexes in ILs is quantitatively shown via photometric measurements using a chromophoric Mo(0) DADS complex in a toluene/[BMIM]OTf biphasic mixture as a model system. It was shown that complexes with ionic liquid (IL) – typical onium salts of sulfonated diazadienes as ligands are strongly retained in an IL phase in contact with a toluene phase, which may make these ligands potentially useful in IL/organic biphasic catalysis.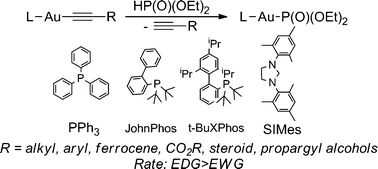 In this HOT Article, US researchers have presented an in depth reactivity study of alkynylgold species and phosphonates. As protodeauration is the main terminating step in gold catalysis, the effect of labile P–H bonds will be of interest to those studying gold catalysis, as well as those studying phosphite chemistry.
In this HOT Article, US researchers have presented an in depth reactivity study of alkynylgold species and phosphonates. As protodeauration is the main terminating step in gold catalysis, the effect of labile P–H bonds will be of interest to those studying gold catalysis, as well as those studying phosphite chemistry.