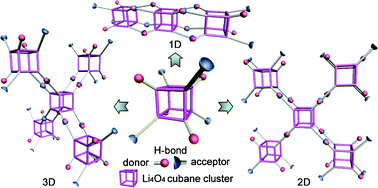
Hydrogen-bond bridges between lithium cubane clusters can give tetrahedral, square planar and linear supramolecular networks.
Pingyun Feng and colleagues report the integration of lithium cubane clusters into 3D supramolecular networks in this communication. Formation of the lithium cubane clusters, which then act as building blocks that are pre-programmed to assemble assorted hydrogen-bonded geometries, can be done in situ, under mild reaction conditions and using readily available chemicals. Key to the success of the strategy is the use of ditopic ligands with both phenol and pyridine functionality. Phenol facilitates the assembly of the cubane cluster and pyridine acts as an H-bond acceptor. In addition, an H-bond donor comes from methanol occupying the fourth coordination site of the lithium atom. Future studies building on this work will look at extending the ligand design to create new supramolecular networks with greater porosity and improved gas sorption properties.
To find out more, download this Dalton Trans. communication today…
Lithium cubane clusters as tetrahedral, square planar, and linear nodes for supramolecular assemblies
Xiang Zhao, Tao Wu, Xianhui Bu and Pingyun Feng
Dalton Trans., 2012
DOI: 10.1039/C1DT11975C
Do also take a look at previous work from the same team:
Hydrogen-bonded boron imidazolate frameworks
Jian Zhang, Tao Wu, Pingyun Feng and Xianhui Bu
Dalton Trans., 2010, 39, 1702-1704
DOI: 10.1039/B924633A