Check out the cover articles in Dalton Transactions issue 19

The outside cover features work from the Leznoff group. Four new [AuBr2(CN)2]−-based coordination polymers, Zn(pyz)(NCMe)2[AuBr2(CN)2]2 (1; pyz = pyrazine), Co(pyz)[AuBr2(CN)2]2·H2O (2) and [M(bipy)2(AuBr2(CN)2)][nBu4N][AuBr2(CN)2]2 (bipy = 4,4′-bipyridine), where M = Co (5) and Zn (6), were synthesized and three of them structurally characterized. 1 forms 1-D chains connected by pyz ligands while isostructural 5 and 6 form 3-D frameworks via [AuBr2(CN)2]− and bipy linkers.
Read more at:
Thermally triggered reductive elimination of bromine from Au(III) as a path to Au(I)-based coordination polymers
Jeffrey S. Ovens and Daniel B. Leznoff
Dalton Trans., 2011, 40, 4140-4146
DOI: 10.1039/C0DT01772H
The inside cover originates from two articles by the Kumar group based on chemosensors.
For more details see:
Ratiometric detection of Hg2+ ions: an allosterically synchronized Hg2+/Li+ switch based on thiacalix[4]crown
Manoj Kumar, Naresh Kumar and Vandana Bhalla
Dalton Trans., 2011, 40, 5170-5175
DOI: 10.1039/C1DT10093A
Structural and magnetic properties of three novel complexes with the versatile ligand 5-methyl-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7(4H)-one
Ana B. Caballero, Antonio Rodríguez-Diéguez, Luis Lezama, Elisa Barea and Juan M. Salas
Dalton Trans., 2011, 40, 5180-5187
DOI: 10.1039/C0DT01416H






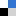




 In this HOT article, a very careful synthetic and catalytic study of the use of di- and trisulfonated phosphines with o, m and o, m, m substitution patterns is described. Pd complexes of these were tested for copolymerizations with polar monomers. This led to a novel anionic phosphine sulphonate Pd(II)-based pre-catalyst salt for polymerisation reactions. Although, polymerisation in the presence of methyl acrylate, acrylonitrile and vinyl acetate led to reduced incorporation values compared to the available literature reports in combination with problems that are attributed to aggregation of the catalyst in most cases, the facile synthesis of chelating highly polar ligands which show high water solubility could be of significant interest for homogeneous catalysis by application in other systems.
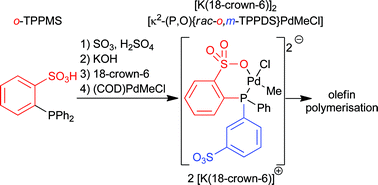
In this HOT article, a very careful synthetic and catalytic study of the use of di- and trisulfonated phosphines with o, m and o, m, m substitution patterns is described. Pd complexes of these were tested for copolymerizations with polar monomers. This led to a novel anionic phosphine sulphonate Pd(II)-based pre-catalyst salt for polymerisation reactions. Although, polymerisation in the presence of methyl acrylate, acrylonitrile and vinyl acetate led to reduced incorporation values compared to the available literature reports in combination with problems that are attributed to aggregation of the catalyst in most cases, the facile synthesis of chelating highly polar ligands which show high water solubility could be of significant interest for homogeneous catalysis by application in other systems.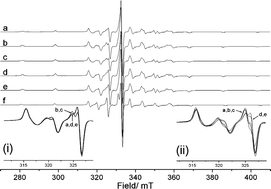 In this HOT article, the authors have extended their work in understanding enantioselective catalysis by coordination compounds. The role of steric hindrance in controlling the binding mode of propylene oxide to a novel vanadyl salen-type complex N,N‘-bis(5-tert-butylsalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamino-vanadium(IV) oxide, [VO(3)], has been investigated using CW/pulse EPR, ENDOR and HYSCORE spectroscopy and compared to that of the parent complex N,N‘-bis(3,5-di-tert-butylsalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamino-vanadium(IV) oxide, [VO(1)]. Removal of the ‘inner tert-butyl groups from the salicylidene rings reduces the steric hindrance between the ligand and epoxide substrate. As a result the selectivity for binding single enantiomers of propylene oxide in these complexes is reversed in [VO(3)] relative to [VO(1)].
In this HOT article, the authors have extended their work in understanding enantioselective catalysis by coordination compounds. The role of steric hindrance in controlling the binding mode of propylene oxide to a novel vanadyl salen-type complex N,N‘-bis(5-tert-butylsalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamino-vanadium(IV) oxide, [VO(3)], has been investigated using CW/pulse EPR, ENDOR and HYSCORE spectroscopy and compared to that of the parent complex N,N‘-bis(3,5-di-tert-butylsalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamino-vanadium(IV) oxide, [VO(1)]. Removal of the ‘inner tert-butyl groups from the salicylidene rings reduces the steric hindrance between the ligand and epoxide substrate. As a result the selectivity for binding single enantiomers of propylene oxide in these complexes is reversed in [VO(3)] relative to [VO(1)]. In this HOT article, the molecular structures of 1,2-closo-P2B10H10 (1) and 1,2-closo-As2B10H10 (2) have been determined by gas electron diffraction and the results obtained compared with those from computation at the MP2/6-31G** level of theory. The first examples of metalladiphosphaboranes and a considerable extension of the range of known metalladiarsaboranes, these compounds being prepared from deboronated derivatives of 1 and 2, respectively, are also reported.
In this HOT article, the molecular structures of 1,2-closo-P2B10H10 (1) and 1,2-closo-As2B10H10 (2) have been determined by gas electron diffraction and the results obtained compared with those from computation at the MP2/6-31G** level of theory. The first examples of metalladiphosphaboranes and a considerable extension of the range of known metalladiarsaboranes, these compounds being prepared from deboronated derivatives of 1 and 2, respectively, are also reported.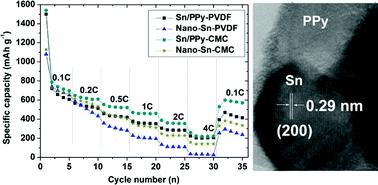 Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have successfully dominated the commercial power supply market for advanced portable electronics. In this regard, metallic Sn has attracted a great deal of interest as an anode material because of its high theoretical capacity offering a significant advantage over the currently used graphite but until now has not been utilized due to the huge volumetric changes during Li-insertion/extraction cycling, which leads to rapid pulverization and poor cyclability of the materials.
Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have successfully dominated the commercial power supply market for advanced portable electronics. In this regard, metallic Sn has attracted a great deal of interest as an anode material because of its high theoretical capacity offering a significant advantage over the currently used graphite but until now has not been utilized due to the huge volumetric changes during Li-insertion/extraction cycling, which leads to rapid pulverization and poor cyclability of the materials. 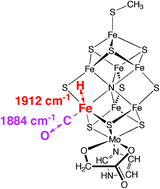 In this HOT article, Ian Dance examines afresh the relationships between CO and H on nitrogenase cofactors following the recent finding that vanadium nitrogenase and modified molybdenum nitrogenase reduce CO to hydrocarbons. In order to assist the interpretation of kinetic infrared spectral data, vibrational frequencies and modes have been calculated for a variety of possible structures in which FeMo-co bears H atoms, or CO ligands, or both.
In this HOT article, Ian Dance examines afresh the relationships between CO and H on nitrogenase cofactors following the recent finding that vanadium nitrogenase and modified molybdenum nitrogenase reduce CO to hydrocarbons. In order to assist the interpretation of kinetic infrared spectral data, vibrational frequencies and modes have been calculated for a variety of possible structures in which FeMo-co bears H atoms, or CO ligands, or both.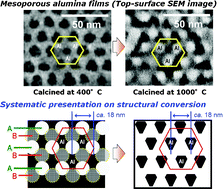 In this HOT article, Wu and Yamauchi et al., reported the synthesis of highly ordered mesoporous alumina thin films existing both as P63/mmc and Fm-3m mesostructures by using triblock copolymer Pluronic P123 as a structure-directing agent and their framework crystallization to γ-alumina phase at 1000 °C. During the crystallization process, large uniaxial shrinkage occurred along the direction perpendicular to the substrate with the retention of horizontal mesoscale periodicity, thereby forming vertically oriented nanopillars on the film surface.
In this HOT article, Wu and Yamauchi et al., reported the synthesis of highly ordered mesoporous alumina thin films existing both as P63/mmc and Fm-3m mesostructures by using triblock copolymer Pluronic P123 as a structure-directing agent and their framework crystallization to γ-alumina phase at 1000 °C. During the crystallization process, large uniaxial shrinkage occurred along the direction perpendicular to the substrate with the retention of horizontal mesoscale periodicity, thereby forming vertically oriented nanopillars on the film surface.