 Amine borane complexes are a promising solution for storing hydrogen, particularly as we move towards a hydrogen economy. Whilst focusing on developing the dehydrogenation of such complexes (namely dimethylamine-borane), scientists from Turkey have shown that you need to think small to think big by preparing a nanoparticle catalyst for the reaction.
Amine borane complexes are a promising solution for storing hydrogen, particularly as we move towards a hydrogen economy. Whilst focusing on developing the dehydrogenation of such complexes (namely dimethylamine-borane), scientists from Turkey have shown that you need to think small to think big by preparing a nanoparticle catalyst for the reaction.
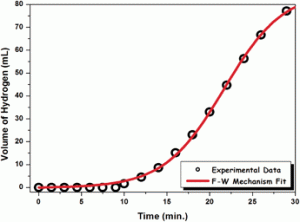
By adding ruthenium (III) chloride to the hydrogen storing dimethlyamine-borane complex, the team found that ruthenium nanoparticles are generated in-situ which further work to catalyse the release of hydrogen from the complex.
Nanosizing the catalyst means a higher proportion of surface atoms are available for the hydrogen-storage complex – the result is greater catalytic activity and faster hydrogen generation.
Read the HOT article now for free… Hydrogen liberation from the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of dimethylamine–borane at room temperature by using a novel ruthenium nanocatalyst
Salim Caliskan, Mehmet Zahmakiran, Feyyaz Durap and Saim Özkar