PCCP is pleased to announce a high-profile themed issue on multiply charged ions (MCIs) in the gas-phase, Guest Edited by Professor Stephen Price (University College London) and Dr Jana Roithová (Charles University, Prague).
Submit to this themed issue – Submission Deadline: 16 May 2011
Fifteen years ago gas-phase multiply-charged ions (MCIs) were viewed as chemical oddities. However, the development of a wide variety of new experimental and theoretical methodologies now means that the unique and unusual properties of these species (both negatively and positively charged) have begun to be revealed: from reactions forming new dicationic rare gas compounds to supramolecular assembly of multiply-charged species in a mass spectrometer.
Our increased understanding of the properties of MCIs allows us to appreciate that their chemistry may be involved in media as varied as fusion plasmas and planetary ionospheres. Scientists are now working on vast range of MCI projects, yet these seemingly rather disparate fields are united because, in all cases, the properties of the MCIs are critically determined by the subtle competition of electrostatic repulsion and chemical bonding.
This issue will highlight the parallel progress and common themes in the chemical physics and physical chemistry of MCIs. The varied topics covered will generate an issue which will appeal to the broad spread of scientists involved with gas-phase MCIs: molecular and chemical physicists, spectroscopists and mass spectrometrists, physical chemists and even inorganic chemists.
Submission details
- You can submit via our online submissions service – please indicate your manuscript is intended for this themed issue.
- Submissions should be high quality manuscripts of original, unpublished research. All submissions will be subject to rigorous peer review
- This issue will be published in late 2011 anddisplayed at relevant conferences to maximise the visibility of the work published.
Comments Off on Multiply charged ions in the gas-phase – call for papers










 View the article on PhysOrg.com
View the article on PhysOrg.com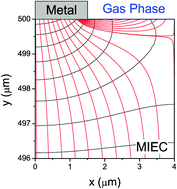
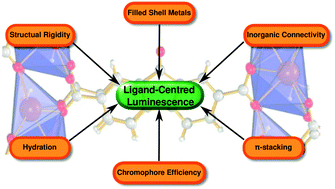 Three novel inorganic–organic framework compounds containing different organic chromophore ligands have been synthesized and evaluated for their use as phosphor materials for solid state lighting and other applications.
Three novel inorganic–organic framework compounds containing different organic chromophore ligands have been synthesized and evaluated for their use as phosphor materials for solid state lighting and other applications. Julian Eastoe and colleagues at the University of Bristol have discovered a new method to extract oil using CO2 in an efficient and environmentally friendly way.
Julian Eastoe and colleagues at the University of Bristol have discovered a new method to extract oil using CO2 in an efficient and environmentally friendly way.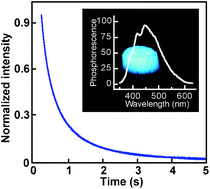 Such mesoporous silica materials, including both powders and monoliths, with strong phosphorescence could find promising applications as low-density and eco-friendly phosphors and optically detectable drug carriers.
Such mesoporous silica materials, including both powders and monoliths, with strong phosphorescence could find promising applications as low-density and eco-friendly phosphors and optically detectable drug carriers.