Urine-powered fuel cells could generate electricity and reclaim essential nutrients directly from human and animal waste, say UK scientists. The development could make wastewater treatment easier and cheaper, and provide an abundant source of locally generated power.
The team, led by Ioannis Ieropolous and John Greenman at the Bristol Robotics Laboratory, developed microbial fuel cells (MFCs) – which use bacteria to break down organic molecules and generate electricity – that could run on the organic molecules found in urine, such as uric acid, creatinine and small peptides.
Finding the right bacteria to munch these molecules was relatively easy – wastewater treatment plants routinely employ bacteria to do the job. But the crucial point, says Ieropoulos, is that the current processes are energy intensive, whereas the fuel cell approach could turn it into an energy-generating process. Getting the urine on the other hand, required a volunteer. ‘It’s one of us,’ quips Greenman, ‘but we’re not going to say which one.’
The bacteria form a robust biofilm on the anode surface of the fuel cell, and pass electrons to the electrode as they respire and metabolise the fuel molecules in the urine. The team have found that smaller cells have higher energy densities, ‘so we’ve followed a path of miniaturisation and multiplication, building stacks of cells,’ says Ieropoulos. An individual cell can produce a current of 0.25mA for 3 days from 25ml of urine, so stacks of hundreds or thousands of cells could run on the amounts of urine available from homes, farms, or public toilets, for example. ‘Initially we’d probably be targeting local microgeneration,’ says Greenman.
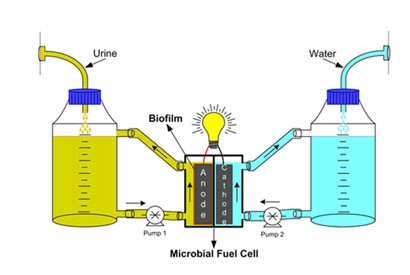
The microbial fuel cell metabolises organic compounds in urine to produce electricity
The lack of solids – which could clog up the fuel cells – in urine compared to more general wastewater gives this system a significant advantage, comments Lars Angenent, director of the agricultural waste management lab at Cornell University in Ithaca, US. But, he points out, there are some issues: ‘Firstly, there is a societal question – do people want to separate their urine?’ Although there are modern toilets that can perform the separation, it would require a social change. ‘Then there is the cost issue – they’ve shown it can be done, but will it be economical?’
Angenent observes that some research has moved from fuel cells towards electrolysis of the urea in wastewater to form hydrogen or hydrogen peroxide. These valuable products help balance the device costs. However, as Ieropolous explains, the bacteria in their fuel cell can’t metabolise urea as fuel, so it could be possible to pass the urine first through an electrolytic cell to generate hydrogen, then through the MFC to generate electricity from the other organics.
As well as generating power, the team’s MFCs could help reclaim essential nutrients from waste, adds Greenman. Urine is particularly troublesome in wastewater treatment, since it not only contains organic compounds, but also high levels of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Treatment plants currently expend significant effort and energy removing these elements from wastewater, as releasing them constitutes environmental pollution in the same way as excess fertiliser leaching from agricultural land – it promotes algal blooms that can choke out rivers and waterways.
The fuel cell bacteria could sequester those salts to grow and divide, but in normal urine the balance of nutrients is wrong – there isn’t enough carbon fuel for them to grow fast enough to take up sufficient amounts of the other elements. ‘But if you balance it by adding a cheap carbon source like acetate,’ says Greenman, ‘all the nitrogen, phosphate and potassium is captured into daughter bacteria, which perfuse out of the MFC and can be filtered out and dug back into the ground as fertiliser.’
Phillip Broadwith
Read the paper from Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics:
Urine utilisation by Microbial Fuel Cells; energy fuel for the future
Ioannis Ieropoulos, John Greenman and Chris Melhuish
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011
DOI: 10.1039/c1cp23213d
 We are delighted to announce that the PCCP themed issue on Aromaticity, electron delocalisation, and related molecular properties has now been published online – take a look today!
We are delighted to announce that the PCCP themed issue on Aromaticity, electron delocalisation, and related molecular properties has now been published online – take a look today!












 We are delighted to announce that the PCCP themed issue on
We are delighted to announce that the PCCP themed issue on 

