Take a look at our HOT articles for the month of June and let us know your thoughts below. Remember, these are free to access for four weeks!
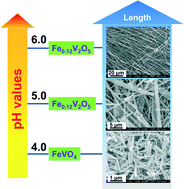
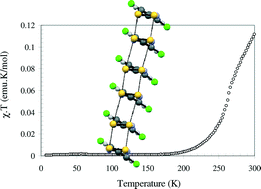
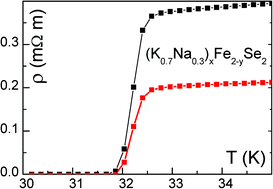
Crystal growth, transport phenomena and two-gap superconductivity in the mixed alkali metal (K1−zNaz)xFe2−ySe2 iron selenide
Maria Roslova, Svetoslav Kuzmichev, Tatiana Kuzmicheva, Yevgeny Ovchenkov, Min Liu, Igor Morozov, Aleksandr Boltalin, Andrey Shevelkov, Dmitry Chareev and Alexander Vasiliev
CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C3CE42664E
Free to access until 30th July 2014
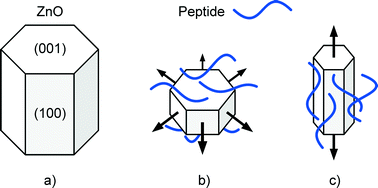
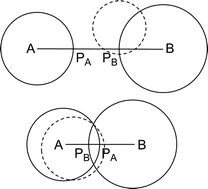
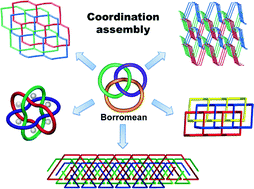
Coordination assembly of Borromean structures
Mei Pan and Cheng-Yong Su
CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4CE00616J
Free to access until 30th July 2014
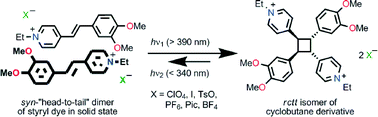
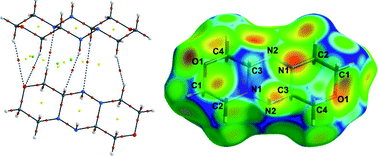
Weak hydrogen and dihydrogen bonds instead of strong N–HO bonds of a tricyclic [1,2,4,5]-tetrazine derivative. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction, theoretical calculations and Hirshfeld surface analysis
Magdalena Owczarek, Irena Majerz and Ryszard Jakubas
CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4CE00571F
Free to access until 15th July 2014
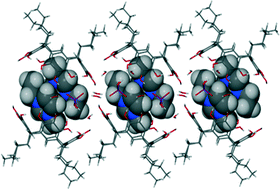
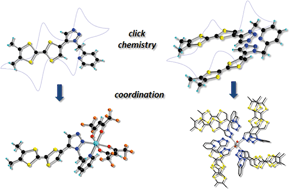
Electroactive tetrathiafulvalene based pyridine-mono and -bis(1,2,3-triazoles) click ligands: synthesis, crystal structures and coordination chemistry
Thomas Biet and Narcis Avarvari
CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4CE00736K
Free to access until 15th July 2014
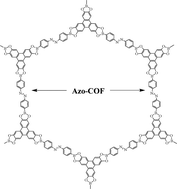
A novel azobenzene covalent organic framework
Jian Zhang, Laibing Wang, Na Li, Jiangfei Liu, Wei Zhang, Zhengbiao Zhang, Nianchen Zhou and Xiulin Zhu
CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4CE00369A
Free to access until 15th July 2014
The direct growth of a WO3 nanosheet array on a transparent conducting substrate for highly efficient electrochromic and electrocatalytic applications
Guo-fa Cai, Jiang-ping Tu, Ding Zhou, Lu Li, Jia-heng Zhang, Xiu-li Wang and Chang-dong Gu
CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4CE00404C
Free to access until 15th July 2014
How to print a crystal structure model in 3D
Teng-Hao Chen, Semin Lee, Amar H. Flood and Ognjen Š. Miljanić
CrystEngComm, 2014, 16, 5488-5493
DOI: 10.1039/C4CE00371C
Free to access until 8th July 2014
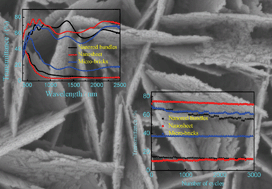
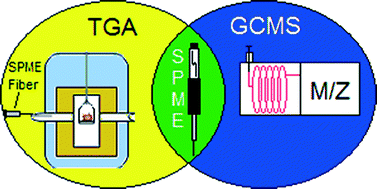
Solid phase microextraction (SPME) combined with TGA as a technique for guest analysis in crystal engineering
Matthew J. Fischer and Alicia M. Beatty
CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4CE00419A
Free to access until 8th July 2014
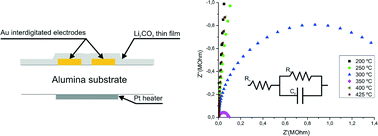
Li2CO3 thin films fabricated by sputtering techniques: the role of temperature on their properties
Lander Rojo, Irene Castro-Hurtado, María C. Morant-Miñana, Gemma G. Mandayo and Enrique Castaño
CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4CE00476K
Free to access until 8th July 2014
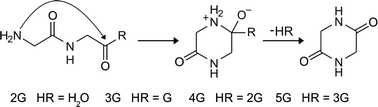
Glycine homopeptides: the effect of the chain length on the crystal structure and solid state reactivity
Aaron J. Smith, Farukh I. Ali and Dmitriy V. Soldatov
CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4CE00630E
Free to access until 8th July 2014
A study of the step-flow growth of the PVT-grown AlN crystals by a multi-scale modeling method
Wei Guo, Julia Kundin, Matthias Bickermann and Heike Emmerich
CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4CE00175C
Free to access until 8th July 2014
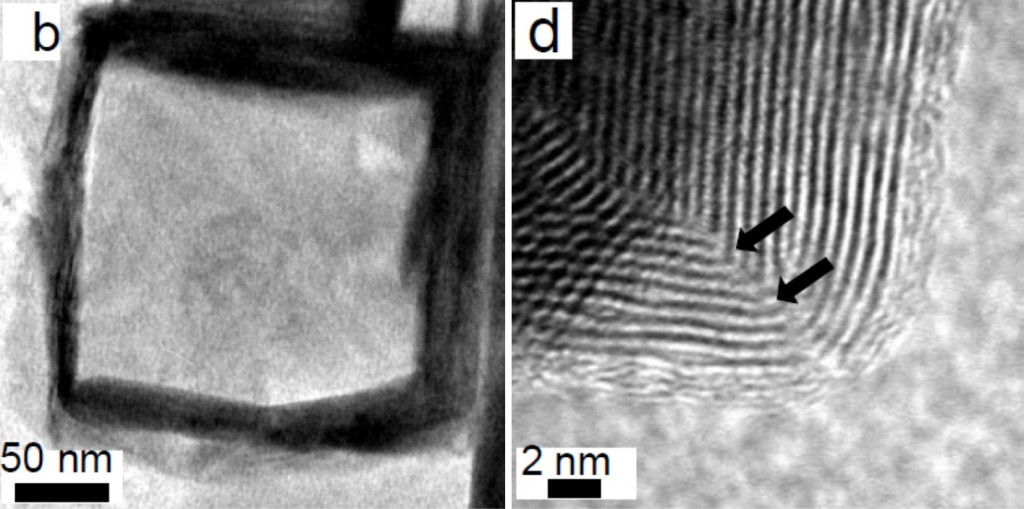
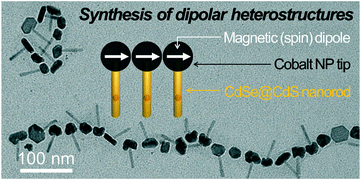
Synthesis of ferromagnetic cobalt nanoparticle tipped CdSe@CdS nanorods: critical role of Pt-activation
Lawrence J. Hill, Nathaniel E. Richey, Younghun Sung, Philip T. Dirlam, Jared J. Griebel, In-Bo Shim, Nicola Pinna, Marc-Georg Willinger, Walter Vogel, Kookheon Char and Jeffrey Pyun
CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4CE00680A
Free to access until 8th July 2014


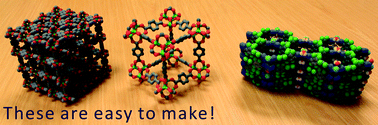








 Gwenda Kyd has a PhD in metallocarborane chemistry from the University of Edinburgh. Other research work includes the spectroscopic study of the structure of glasses and organometallic electron-transfer reactions and the preparation of new inorganic phosphors. She has recently published a book on chemicals from plants.
Gwenda Kyd has a PhD in metallocarborane chemistry from the University of Edinburgh. Other research work includes the spectroscopic study of the structure of glasses and organometallic electron-transfer reactions and the preparation of new inorganic phosphors. She has recently published a book on chemicals from plants.