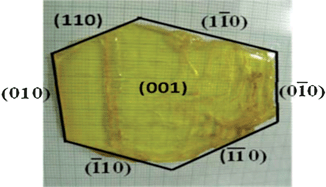
In this CrystEngComm Hot article, Sunil Verma and co-workers have produced a large single crystal of lithium pnitrophenolate trihydrate, which can be used as a non-linear optical material.
Non-linear optical materials can be used in lasers, and organic NLO materials are particularly desirable because they have higher non-linearity and better laser damage resistance when compared to inorganic materials.
This article is significant because the authors have managed to grow a large size crystal, which is normally difficult due to the weakness of the van der Waals and hydrogen bonds holding the molecules together.
Read the full article to find out more about the slow cooling solution growth method used…
Solubility, crystal growth, morphology, crystalline perfection and optical homogeneity of lithium p-nitrophenolate trihydrate, a semiorganic NLO crystal
S. Dinakaran, Sunil Verma and S. Jerome Das
CrystEngComm, 2011, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C0CE00663G, Paper
READ FOR FREE until 3rd March 2011











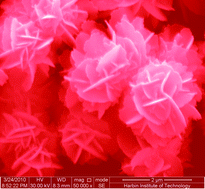
 Morphology of magneto-electrodeposited Cu2O microcrystals
Morphology of magneto-electrodeposited Cu2O microcrystals