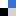Self-assembled, monodispersed, flower-like γ-AlOOH hierarchical superstructures for efficient and fast removal of heavy metal ions from water
Yong-Xing Zhang, Yong Jia, Zhen Jin, Xin-Yao Yu, Wei-Hong Xu, Tao Luo, Bang-Jing Zhu, Jin-Huai Liu and Xing-Jiu Huang
CrystEngComm, 2012,14, 3005-3007
In this paper, Yong-Xing Zhang et. al. report the synthesis of self-assembled, monodispersed, flower-like γ-AlOOH hierarchical superstructures for the fast and efficient removal of heavy metal ions Pb(II) and Hg(II) from water via adsorption. These superstructures have been synthesized with BET surface area of 145 m2/g. The authors have shown that over 99.0% of Pb(II) and Hg(II) ions can be removed from aqueous solutions by the flower-like γ-AlOOH within five minutes. Also, as confirmed from adsorption isotherms, the maximal adsorption is ca. 124 mg/g for Pb(II) and 131 mg/g for Hg(II). This work promises to be very useful towards addressing water contamination issues.
Crystallographic analysis of CO2 sorption state in seemingly nonporous molecular crystal of azacalix[4]arene tetramethyl ether exhibiting highly selective CO2 uptake
Hirohito Tsue, Hiroki Takahashi, Koichi Ishibashi, Rikako Inoue, Shun Shimizu, Daisuke Takahashi and Rui Tamura
CrystEngComm, 2012, 14, 1021-1026
This paper by Hirohito Tsue et al. describes the highly selective CO2 sorption by seemingly nonporous crystals of azacalix[4]arene at low temperatures. Single crystal X-ray crystallography was used to carry out an analysis of the CO2 sorption state at the atomic level, and it was found that weak intermolecular CH/O-interactions had a major role in stabilizing CO2 molecules inside the crystal.
Metal–organic frameworks: Promising materials for enhancing electrochemical properties of nanostructured Zn2SnO4 anode in Li-ion batteries
Xiangzhen Zheng, Yafeng Li, Yuxia Xu, Zhensheng Hong and Mingdeng Wei
CrystEngComm, 2012, 14, 2112-2116
This paper by Wei et al. describes how metal-organic frameworks can improve the electrochemical properties of Li-ion batteries (LIBs). Some interesting highlights of the paper include:
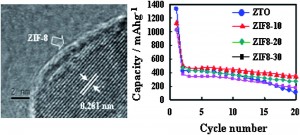
1. This is the first report of the formation of this core/shell structure oin ZTO/ZIF-8 nanocomposites.
2. ZTO/ZIF-8 nanocomposites exhibited larger charge capacities and good cycling performance in LIBs.
3. Porous ZIF-8 on the electrodes helps to release the stress caused by the drastic volume expansion during Li–Sn alloying/de-alloying process, thus enhancing the electrochemical performance of the LIBs.
Hydrothermal aggregation induced crystallization: a facial route towards polycrystalline graphite quantum dots with blue photoluminescence
Zehui Zhang and Peiyi Wu
CrystEngComm, 2012, 14, 7149-7152
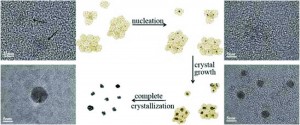
In this paper, Wu et al. demonstrated a one step, environmentally friendly method to synthesize graphite quantum dots from graphene oxide, using NH3 as the passivation agent. A thorough study of the growth mechanism of graphite quantum dots, including a time-dependent experiment, was presented. The authors also explained the role of NH3 in enhancing the blue luminescence property of the quantum dots.
NiO nanomaterials: controlled fabrication, formation mechanism and the application in lithium-ion battery
Jianmin Ma, Jiaqin Yang, Lifang Jiao, Yuhua Mao, Taihong Wang, Xiaochuan Duan, Jiabiao Lian and Wenjun Zheng
CrystEngComm, 2012, 14, 453-459
This paper is focused on NiO nanomaterials: controlled fabrication, formation mechanism and their application in lithium-ion batteries.
The authors obtained various NiO nanostructures through annealing the corresponding β-Ni(OH)2 nanostructures at high temperatures. The variety of morphologies in the NiO nanostructures obtained in this work also provided an opportunity to understand the relation between the morphology of the nanostructure and its electrochemical properties.
In terms of the electrochemical performance, these materials have a high initial discharging capacity, although there is still room for improvement in the stability of the material over many charge-discharge cycles.
Conversion of azide to primary amine via Staudinger reaction in metal–organic frameworks
Shunjiro Nagata, Hiroki Sato, Kouta Sugikawa, Kenta Kokado and Kazuki Sada
CrystEngComm, 2012,14, 4137-4141
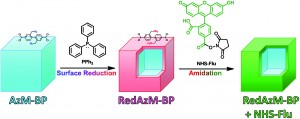
In this paper, Kazuki Sada et al. describes the facile conversion of azide to primary amine in metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). This post-synthetic surface-selective modification is a useful method for the preparation of MOFs with core-shell structures.
Some important findings include:
1. The conversion of the azide groups into amine by treatment of triphenylphosphine in the presence of water is a new chemical reaction for post-synthetic modification of MOFs.
2. A shorter reaction time induced partial reduction of the azide groups with the preservation of high crystallinity, whereas a longer reaction time induced complete conversion of azide groups.
3. The reactivity of the resulting primary amine groups was confirmed by the further condensation of an activated ester.
 Rahul Banerjee received his PhD degree from University of Hyderabad, Hyderabad in 2006 under the supervision of Prof. Gautam R. Desiraju. After postdoctoral work in UCLA with Prof. Omar M. Yaghi (2006-2008), he joined CSIR-National Chemical Laboratory, Pune, India in 2008 as a Scientist. His research interests include the study of structural chemistry with a focus on chemical synthesis to design new materials for hydrogen storage, carbon sequestration and catalysis. Additionally, his group is also engaged in design and synthesis of lightweight materials for storage, capture and proton conduction. Dr. Banerjee is an Editorial board member and an Associate Editor of CrystEngComm. He also served as a co-editor of Acta Crystallographica Section E till 2012.
Rahul Banerjee received his PhD degree from University of Hyderabad, Hyderabad in 2006 under the supervision of Prof. Gautam R. Desiraju. After postdoctoral work in UCLA with Prof. Omar M. Yaghi (2006-2008), he joined CSIR-National Chemical Laboratory, Pune, India in 2008 as a Scientist. His research interests include the study of structural chemistry with a focus on chemical synthesis to design new materials for hydrogen storage, carbon sequestration and catalysis. Additionally, his group is also engaged in design and synthesis of lightweight materials for storage, capture and proton conduction. Dr. Banerjee is an Editorial board member and an Associate Editor of CrystEngComm. He also served as a co-editor of Acta Crystallographica Section E till 2012.


![Crystallographic analysis of CO2 sorption state in seemingly nonporous molecular crystal of azacalix[4]arene tetramethyl ether exhibiting highly selective CO2 uptake Crystallographic analysis of CO2 sorption state in seemingly nonporous molecular crystal of azacalix[4]arene tetramethyl ether exhibiting highly selective CO2 uptake](https://blogs.rsc.org/ce/files/2013/10/c1ce06126g-ga-293x300.jpg)