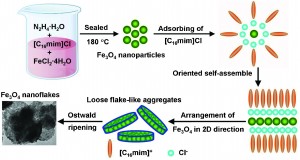
Self-assembled Fe3O4 superstructures have unique electric and magnetic properties, such as allowing the material to exceed the ‘‘superparamagnetic limit’’ found in Fe3O4 with a less well defined structure. Using a novel way of synthesising Fe3O4 nanoflakes via an ionic liquid-assisted solvothermal process, Xiaodi Liu and colleagues have made self-assembled Fe3O4 structures from nanoparticles. These nanoflakes have a good monodispersity and magnetic properties that are not seen in material made by other synthetic methods, making them good candidates for applications such as high density magnetic recording.
In this study, the authors have also explored how different growth conditions affect the final structure, thus providing a method for optimising the process for making other self-assembled nanomaterials using ionic liquids.
Find out more by downloading their paper:
Ionic liquid-assisted solvothermal synthesis of oriented self-assembled Fe3O4 nanoparticles into monodisperse nanoflakes
Xiaodi Liu, Xiaochuan Duan, Qing Qin, Qinglun Wang and Wenjun Zheng
CrystEngComm, 2013, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C3CE00035D, Communication