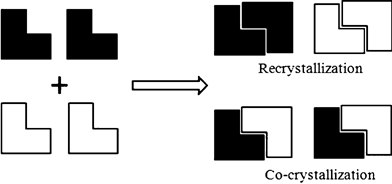
Co-crystallisation is an important tool for establishing the importance of intermolecular interactions in the solid state. One strategy adopted by Christer Aakeröy and his team at Kansas State University is to examine whether crystallisation of two molecules results in a homomeric interaction (essentially recrystallisation) or a heteromeric interaction (co-crystallisation). Combining 2-aminopyrazine derivatives with numerous carboxylic acids, the team discovered that they could attribute the success of co-crystallisation with electrostatic charges on the hydrogen bond acceptor sites – as they predicted, the lower the charge, the lower the supramolecular yield of the reaction.
Although hydrogen bonding is a fundamental concept taught to us in the classroom, we still have a lot to learn!
Read the article to find out more…
Exploring the structural landscape of 2-aminopyrazines via co-crystallizations
Christer B. Aakeröy, Prashant D. Chopade, Claudia Ganser, Arbin Rajbanshi and John Desper