The latest issue of Analyst is online with three cover articles for you to enjoy.
Chung et al., Analyst, 2012, 137, 4921
The very informative front cover comes from Yu-Chang Tyan and Tze-Wen Chung from the National Yunlin University of Science and Technology and Kaohsiung Medical University, respectively, and colleagues from Taiwan. In their study they proposed a new approach for the detection of proteins to assess the response of fibroblasts to a material surface. Biomaterials play an important role in regenerative medicine and drug delivery, therefore the interactions between biomaterial surfaces and cells are important to characterize cell proliferation, differentiation and regeneration of tissues.
Assessing the responses of cellular proteins induced by hyaluronic acid-modified surfaces utilizing a mass spectrometry-based profiling system: Over-expression of CD36, CD44, CDK9, and PP2A
Ming-Hui Yang, Shiang-Bin Jong, Chi-Yu Lu, Yu-Fen Lin, Pei-Wen Chiang, Yu-Chang Tyan and Tze-Wen Chung
Analyst, 2012, 137, 4921-4933
DOI: 10.1039/C2AN35368G

Kaminskyj et al., Analyst, 2012, 137, 4934
We head to Canada for our inside front cover. Kathleen M. Gough and Susan G. W. Kaminskyj from the University of Manitoba and the University of Saskatchewan, together with colleagues have been studying the filamentous fungi Aspergillus. This fungi can can affect humans through their roles in biotechnology and recycling, and can also be responsible for disease.
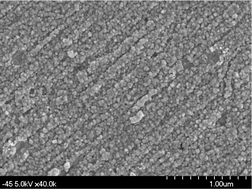
What they have discovered is that Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) can provide chemical information on materials that are in close contact with appropriate metal substrates, in this case nanopatterned gold surfaces and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). They have created conditions for AuNP formation within and on the surface of Aspergillus nidulans hyphae in order to explore their potential for SERS analysis.
Proof-of-principle for SERS imaging of Aspergillus nidulans hyphae using in vivo synthesis of gold nanoparticles
Martin A. Prusinkiewicz, Fatemeh Farazkhorasani, James J. Dynes, Jian Wang, Kathleen M. Gough and Susan G. W. Kaminskyj
Analyst, 2012, 137, 4934-4942
DOI: 10.1039/C2AN35620A
Zhang et al., Analyst, 2012, 137, 4917
On the back cover of this month’s issue we showcase the work contributed by Weidong He, and Xiao Lin at the Vanderbilt Institute of Nanoscale Science and Technology, and the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences who together with colleagues have studied the analytical expression of Coulombic interaction between a nanorod and a nanoparticle.
The evaluation of Coulombic interaction in the oriented-attachment growth of colloidal nanorods
Weidong He, Junhao Lin, Xiao Lin, Ning Lu, Ming Zhou and Kelvin H. L. Zhang
Analyst, 2012, 137, 4917-4920
DOI: 10.1039/C2AN35950B
All of these papers will be free to access for 6 weeks. So why not click through and have a read.