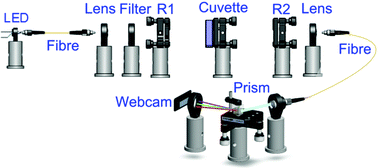
Low cost webcam based prism spectrometer
Techniques such as cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) have greatly enhanced the sensitivity in traditional absorption spectroscopy methods. Although CRDS can detect analytes in very small concentrations in solution, it requires expensive and complex instrumentation, which has restricted its widespread implementation. Alternatively, broadband cavity enhanced absorption spectroscopy (BBCEAS) has emerged to overcome some of these limitations. These adjustments allow for multiplexed data collection and improved resolution.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge, UK, have constructed a BBCEAS apparatus using relatively simple components and achieved sensitivity levels similar to much more expensive systems. Using a well-studied process, the Griess Assay, they measured different concentrations of nitrite and the dye Rhodamine 6 G with a system that contained a low cost prism spectrometer and a webcam detector. The limits of detection were found to be 3.7 nM (nitrite) and 850 pM (Rhodamine), and by adding a better detector, these can further be improved upon.
To read the full article, please access the link below. This paper will be free to read for the next three weeks:
High sensitivity liquid phase measurements using broadband cavity enhanced absorption spectroscopy (BBCEAS) featuring a low cost webcam based prism spectrometer
Zhechao Qu, Julia Engstrom, Donald Wong, Meez Islam and Clemens F. Kaminski
Analyst, 2013,138, 6372-6379
DOI: 10.1039/C3AN01441J