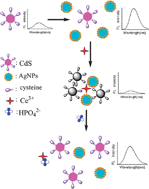
Schematic interaction between Ce3+ and phosphate
Guang-Li Wang and co-workers, from the Jiangnan University, China, have developed an assay to detect the level of phosphate in water.
Ce3+ ions are used to aggregate citrate-capped silver nanoparticles with cysteine-capped quantum dots, thereby causing efficient quenching of the fluorescence signal. However, when phosphate is introduced to the system it interacts with the Ce3+ ions causing the quenched aggregates to redisperse and switching the fluorescent signal from “off” to “on”. This work has potential applications for the environmental analysis of groundwater.
To read more about this work, please access this Analyst HOT article below. It will be free to read until March 8th.
Novel switchable sensor for phosphate based on the distance-dependant fluorescence coupling of cysteine-capped cadmium sulfide quantum dots and silver nanoparticles
Guang-Li Wang , Huan-Jun Jiao , Xiao-Ying Zhu , Yu-Ming Dong and Zai-Jun Li
Analyst, 2013, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C3AN36878E